Spatial characterization of hot melt extruded dispersion systems using thermal atomic force microscopy methods: the effects of processing parameters on phase separation
- PMID: 24554116
- PMCID: PMC4062809
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-013-1279-x
Spatial characterization of hot melt extruded dispersion systems using thermal atomic force microscopy methods: the effects of processing parameters on phase separation
Abstract
Purpose: In this study we explore the use of nano-scale localized thermal analysis (LTA) and transition temperature microcopy (TTM) as a novel combined approach to studying phase separation in HME dispersions of cyclosporine A in Eudragit EPO.
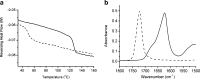
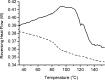
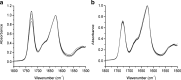
Methods: Modulated temperature differential scanning calorimetry (MTDSC), attenuated total reflectance FTIR spectroscopy, nano-LTA and TTM were performed on raw materials and dispersions prepared by hot melt extrusion (HME) and spin coating. For samples prepared by HME, two mixing temperatures (110°C and 150°C) and residence times (5 and 15 min) were investigated.
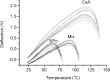
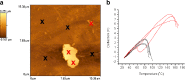
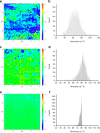
Results: Spin coated samples showed an intermediate T g for the mixed systems consistent with molecular dispersion formation. The HME samples prepared at 110°C showed evidence of inhomogeneity using MTDSC and FTIR, while those produced at 150°C h showed evidence for the formation of a single phase system using MTDSC. The nanothermal methods, however, indicated the presence of phase separated cyclosporine A at the higher preparation temperature while the TTM was able to map regions of differing penetration temperatures, indicating the presence of compositionally inhomogeneous regions in all but the high processing temperature/high residence time samples.
Conclusions: TTM is a potentially important new method for studying phase separation and that such separation may remain undetected or poorly understood using conventional bulk analytical techniques.
Figures
References
-
- Djuris J, Nikolakakis I, Ibric S, Djuric Z, Kachrimanis K. Preparation of carbamazepine-Soluplus (R) solid dispersions by hot-melt extrusion, and prediction of drug-polymer miscibility by thermodynamic model fitting. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013;84(1):228–237. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2012.12.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

