Outcomes of extremely low birthweight infants with acidosis at birth
- PMID: 24554564
- PMCID: PMC4274605
- DOI: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-304179
Outcomes of extremely low birthweight infants with acidosis at birth
Abstract
Objectives: To test the hypothesis that acidosis at birth is associated with the combined primary outcome of death or neurodevelopmental impairment (NDI) in extremely low birthweight (ELBW) infants, and to develop a predictive model of death/NDI exploring perinatal acidosis as a predictor variable.
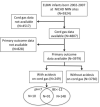
Study design: The study population consisted of ELBW infants born between 2002 and 2007 at National Institute of Child Health and Development (NICHD) Neonatal Research Network hospitals. Infants with cord blood gas data and documentation of either mortality prior to discharge or 18-22 month neurodevelopmental outcomes were included. Multiple logistic regression analysis was used to determine the contribution of perinatal acidosis, defined as a cord blood gas with a pH<7 or base excess (BE) <-12, to death/NDI in ELBW infants. In addition, a multivariable model predicting death/NDI was developed.
Results: 3979 patients were identified of whom 249 had a cord gas pH<7 or BE<-12 mEq/L. 2124 patients (53%) had the primary outcome of death/NDI. After adjustment for confounding variables, pH<7 and BE<-12 mEq/L were each significantly associated with death/NDI (OR=2.5 (1.6, 4.2) and OR=1.5 (1.1, 2.0), respectively). However, inclusion of pH or BE did not improve the ability of the multivariable model to predict death/NDI.
Conclusions: Perinatal acidosis is significantly associated with death/NDI in ELBW infants. Perinatal acidosis is infrequent in ELBW infants, however, and other factors are more important in predicting death/NDI.
Keywords: Neonatology; Neurodevelopment.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures
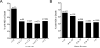
Comment in
-
Prediction models for neonatal outcomes: are they useful? Are they feasible?Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014 Jul;99(4):F255-6. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-305700. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2014. PMID: 24668835 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wilson-Costello D. Is there evidence that long-term outcomes have improved with intensive care? Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2007;12(5):344–54. - PubMed
-
- Marlow N, Wolke D, Bracewell MA, et al. Neurologic and developmental disability at six years of age after extremely preterm birth. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(1):9–19. - PubMed
-
- Vohr BR, Wright LL, Poole WK, et al. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants <32 weeks' gestation between 1993 and 1998. Pediatrics. 2005;116(3):635–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U10 HD27851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053124/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- 5U10HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR24160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021385/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR44/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025764/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53119/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR59/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053119/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR6022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53124/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21364/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD34216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR70/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD36790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000042/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD087229/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40521/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR125/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR633/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53109/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD53089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27871/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR7122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040689/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040492/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR64/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027904/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD021397/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27856/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD27853/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR39/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR30/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD40461/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024160/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000142/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR007122/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD027851/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 HD027880/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR80/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR16587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR750/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR8084/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR25764/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR54/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR997/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD21373/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000064/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR32/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD034216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD036790/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR24139/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD040498/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR006022/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001067/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HD053089/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
