Feasibility of nephron-sparing surgery in giant oncocytoma
- PMID: 24554983
- PMCID: PMC3926935
- DOI: 10.5489/cuaj.1552
Feasibility of nephron-sparing surgery in giant oncocytoma
Abstract
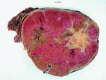
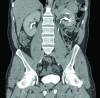
Oncocytomas represent 3 to 7% of renal masses and behave as benign tumours. Nephron-sparing procedures are preferred for biopsy confirmed lesions; however, giant oncocytomas have been generally treated by radical nephrectomy. We report the first case of partial nephrectomy in a 45-year-old man who presented with a 20-cm oncocytoma. At the 1 year follow-up, he had a normal functioning kidney. Despite the difficulty of this procedure, partial nephrectomy for very large benign tumours can be considered in appropriately selected young patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bilateral synchronous renal oncocytoma: a case report and review.Ann Acad Med Singap. 2001 Nov;30(6):642-5. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2001. PMID: 11817296
-
Asymptomatic Giant Right Renal Oncocytoma: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Jan 24;15(1):e34129. doi: 10.7759/cureus.34129. eCollection 2023 Jan. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 36843740 Free PMC article.
-
Robotic-assisted transperitoneal nephron-sparing surgery for small renal masses with associated surgical procedures: surgical technique and preliminary experience.Updates Surg. 2013 Sep;65(3):183-90. doi: 10.1007/s13304-013-0209-0. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Updates Surg. 2013. PMID: 23619828
-
A metachronous, atypical, multifocal renal oncocytoma with a concomitant renal cell carcinoma of the contralateral side and bilateral multifocal oncocytomas: two case reports and review of literature.ScientificWorldJournal. 2005 Jul 20;5:545-9. doi: 10.1100/tsw.2005.73. ScientificWorldJournal. 2005. PMID: 16075151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nephron-sparing surgery--strategies for partial nephrectomy in renal cell carcinoma.Scand J Surg. 2004;93(2):126-31. doi: 10.1177/145749690409300207. Scand J Surg. 2004. PMID: 15285564 Review.
References
-
- Morra MN, Das S. Renal oncocytoma: A review of histogenesis, histopathology, diagnosis and treatment. J Urol. 1993;150:295–302. - PubMed
-
- Cochand-Priollet B, Molinie V, Bougaran J, et al. Renal chromophobe cell carcinoma and oncocytoma. A comparative morphologic, histochemical, and immunohistochemical study of 124 cases. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1997;121:1081–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
