DanQi Pill protects against heart failure through the arachidonic acid metabolism pathway by attenuating different cyclooxygenases and leukotrienes B4
- PMID: 24555740
- PMCID: PMC3933388
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-67
DanQi Pill protects against heart failure through the arachidonic acid metabolism pathway by attenuating different cyclooxygenases and leukotrienes B4
Abstract
Background: Chinese herbal formulae are composed of complex components and produce comprehensive pharmacological effects. Unlike chemical drugs that have only one clear single target, the components of Chinese herbal formulae have multiple channels and targets. How to discover the pharmacological targets of Chinese herbal formulae and their underlying molecular mechanism are still under investigation.
Methods: DanQi pill (DQP), which is one of the widely prescribed traditional Chinese medicines, is applied as an example drug. In this study, we used the drug target prediction model (DrugCIPHER-CS) to examine the underlying molecular mechanism of DQP, followed by experimental validation.
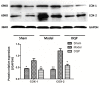
Results: A novel therapeutic effect pattern of DQP was identified. After determining the compounds in DQP, we used DrugCIPHER-CS to predict their potential targets. These potential targets were significantly enriched in well-known cardiovascular disease-related pathways. For example, the biological processes of neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, calcium-signaling pathway, and aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis were involved. A new and significant pathway, arachidonic acid (AA) metabolism, was also identified in this study. This predicted pathway alteration was validated with an animal model of heart failure (HF). Results show that DQP had effect both on thromboxane B2 (TXB2) and Prostaglandin I2 (PGI2) in different patterns. It can down-regulate the TXB2 and up-regulate the PGI2 in diverse way. Remarkably, it also had effect on cyclooxygenase (COX)-1 and COX2 by suppressing their levels, which may be the critical and novel mechanism of cardiacprotective efficacy for DQP. Furthermore, leukotrienes B4 (LTB4) receptor, another key molecule of AA metabolism which finally mediated gastrotoxic leukotrienes, was also reduced by DQP.
Conclusions: The combination of drug target prediction and experimental validation provides new insights into the complicated mechanism of DQP.
Figures



References
-
- Panza JA, Holly TA, Asch FM, She L, Pellikka PA, Velazquez EJ, Lee KL, Borges-Neto S, Farsky PS, Jones RH, Berman DS, Bonow RO. Inducible myocardial ischemia and outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease and left ventricular dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;61:1860–1870. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.02.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li X, Zhang J, Huang J, Ma A, Yang J, Li W, Wu Z, Yao C, Zhang Y, Yao W, Zhang B, Gao R. Efficacy and Safety of Qili Qiangxin Capsules for Chronic Heart Failure Study Group. A multicenter randomized double-blind parallel-group placebo-controlled study of the effects of qili qiangxin capsules in patients with chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:065–1072. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

