Serum total hCGβ level is an independent prognostic factor in transitional cell carcinoma of the urothelial tract
- PMID: 24556622
- PMCID: PMC3974095
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2014.89
Serum total hCGβ level is an independent prognostic factor in transitional cell carcinoma of the urothelial tract
Abstract
Background: Serum total human chorionic gonadotrophin β subunit (hCGβ) level might have prognostic value in urothelial transitional cell carcinoma (TCC) but has not been investigated for independence from other prognostic variables.
Methods: We utilised a clinical database of patients receiving chemotherapy between 2005 and 2011 for urothelial TCC and an independent cohort of radical cystectomy patients for validation purposes. Prognostic variables were tested by univariate Kaplan-Meier analyses and log-rank tests. Statistically significant variables were then assessed by multivariate Cox regression. Total hCGβ level was dichotomised at < vs ≥2 IU l(-1).
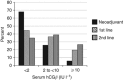
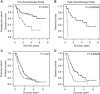
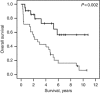
Results: A total of 235 chemotherapy patients were eligible. For neoadjuvant chemotherapy, established prognostic factors including low ECOG performance status, normal haemoglobin, lower T stage and suitability for cisplatin-based chemotherapy were associated with favourable survival in univariate analyses. In addition, low hCGβ level was favourable when assessed either before (median survival not reached vs 1.86 years, P=0.001) or on completion of chemotherapy (4.27 vs 0.42 years, P=0.000002). This was confirmed in multivariate analyses and in patients receiving first- and second-line palliative chemotherapy, and in a radical cystectomy validation set.
Conclusions: Serum total hCGβ level is an independent prognostic factor in patients receiving chemotherapy for urothelial TCC in both curative and palliative settings.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The prognostic role of preoperative serum albumin/globulin ratio in patients with bladder urothelial carcinoma undergoing radical cystectomy.Urol Oncol. 2016 Nov;34(11):484.e1-484.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.05.024. Epub 2016 Jun 21. Urol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27341738
-
Impact of Routine Laboratory Parameters in Patients Undergoing Radical Cystectomy for Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder: A Long-Term Follow-Up.Urol Int. 2020;104(7-8):551-558. doi: 10.1159/000506263. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Urol Int. 2020. PMID: 32114587
-
Improved 5-Factor Prognostic Classification of Patients Receiving Salvage Systemic Therapy for Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma.J Urol. 2016 Feb;195(2):277-82. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2015.07.111. Epub 2015 Aug 17. J Urol. 2016. PMID: 26292040 Free PMC article.
-
Timing cystectomy and perioperative chemotherapy in the treatment of muscle invasive bladder cancer.Can J Urol. 2006 Jun;13 Suppl 3:48-53. Can J Urol. 2006. PMID: 16818012 Review.
-
[Chemotherapy for urothelial cancer of the bladder--update 2012].Aktuelle Urol. 2012 Dec;43(6):412-9. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1327699. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Aktuelle Urol. 2012. PMID: 23196781 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Beta-human chorionic gonadotropin, carbohydrate antigen 19-9, cancer antigen 125, and carcinoembryonic antigen as prognostic and predictive biological markers in bladder cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 23;14:1479988. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1479988. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39763612 Free PMC article.
-
Progesterone limits the tumor-promoting effects of the beta-subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin via non-nuclear receptors.iScience. 2022 Jun 3;25(7):104527. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104527. eCollection 2022 Jul 15. iScience. 2022. PMID: 35754725 Free PMC article.
-
Chorionic Gonadotropin Beta 7 is a marker of immune evasion in cancer.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 2:2025.05.28.656535. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.28.656535. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40501795 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Recent Advances in the Classification of Bladder Cancer - Updates from the 5th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of the Urinary and Male Genital Tumors.Bladder Cancer. 2023 Mar 31;9(1):1-14. doi: 10.3233/BLC-220106. eCollection 2023. Bladder Cancer. 2023. PMID: 38994481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unusual Faces of Bladder Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Dec 10;12(12):3706. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123706. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33321728 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Advanced Bladder Cancer (ABC) Meta-analysis Collaboration Adjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data Advanced Bladder Cancer (ABC) Meta-analysis Collaboration. Eur Urol. 2005;48 (2:189–199. - PubMed
-
- Advanced Bladder Cancer (ABC) Meta-analysis Collaboration Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer: update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data advanced bladder cancer (ABC) meta-analysis collaboration. Eur Urol. 2005;48 (2:202–205. - PubMed
-
- Bajorin DF, Dodd PM, Mazumdar M, Fazzari M, McCaffrey JA, Scher HI, Herr H, Higgins G, Boyle MG. Long-term survival in metastatic transitional-cell carcinoma and prognostic factors predicting outcome of therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17 (10:3173–3181. - PubMed
-
- Cole LA, Butler S. Hyperglycosylated hCG, hCGbeta and hyperglycosylated hCGbeta: interchangeable cancer promoters. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;349 (2:232–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

