The role of statins in erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 24556747
- PMCID: PMC4023379
- DOI: 10.4103/1008-682X.123678
The role of statins in erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
To evaluate the effect of statins for erectile dysfunction (ED), a systematic review of the literature was conducted in the Cochrane Library, Embase and PubMed from the inception of each database to June 2013. Only randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing treatment for ED with statins were identified. Placebo RCTs with the International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) as the outcome measure were eligible for meta-analysis. A total of seven RCTs including two statins with a total of 586 patients strictly met our criteria for systematic review and five of them qualified for the meta-analysis. A meta-analysis using a random effects model showed that statins were associated with a significant increase in IIEF-5 scores (mean difference (MD): 3.27; 95% confidential interval (CI):1.51 to 5.02; P < 0.01) and an overall improvement of lipid profiles including total cholesterol (MD: -1.08; 95% CI: -1.68 to -0.48; P < 0.01), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (MD: -1.43; 95% CI: -2.07 to -0.79; P < 0.01), high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol (MD: 0.24; 95% CI: 0.13 to 0.35; P < 0.01) and triglycerides (TGs) (MD: -0.55; 95% CI: -0.61 to -0.48; P < 0.01). In summary, our study revealed positive consequences of these lipid-lowering drugs on erectile function, especially for nonresponders to phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5Is). However, it has been reported that statin therapy may reduce levels of testosterone and aggravate symptoms of ED. Therefore, larger, well-designed RCTs are needed to investigate the double-edged role of statins in the treatment of ED.
Figures
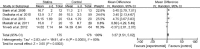
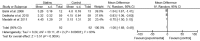
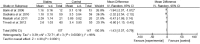
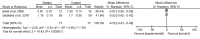
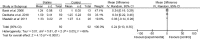
References
-
- Hatzimouratidis K, Amar E, Eardley I, Giuliano F, Hatzichristou D, et al. , European Association of Urology. Guidelines on male sexual dysfunction: erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation. Eur Urol. 2010;57:804–14. - PubMed
-
- Selvin E, Burnett AL, Platz EA. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in the US. Am J Med. 2007;120:151–7. - PubMed
-
- Sullivan ME, Keoghane SR, Miller MA. Vascular risk factors and erectile dysfunction. BJU Int. 2001;87:838–45. - PubMed
-
- Azadzoi KM, Goldstein I, Siroky MB, Traish AM, Krane RJ, et al. Mechanisms of ischemia-induced cavernosal smooth muscle relaxation impairment in a rabbit model of vasculogenic erectile dysfunction. J Urol. 1998;160:2216–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

