Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- PMID: 24556840
- PMCID: PMC4240281
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3758
Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Abstract
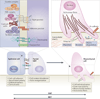
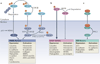
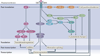
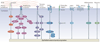
The transdifferentiation of epithelial cells into motile mesenchymal cells, a process known as epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), is integral in development, wound healing and stem cell behaviour, and contributes pathologically to fibrosis and cancer progression. This switch in cell differentiation and behaviour is mediated by key transcription factors, including SNAIL, zinc-finger E-box-binding (ZEB) and basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors, the functions of which are finely regulated at the transcriptional, translational and post-translational levels. The reprogramming of gene expression during EMT, as well as non-transcriptional changes, are initiated and controlled by signalling pathways that respond to extracellular cues. Among these, transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) family signalling has a predominant role; however, the convergence of signalling pathways is essential for EMT.
Figures
References
-
- Hay ED. An overview of epithelio-mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat. 1995;154:8–20. - PubMed
-
- Thiery JP, Sleeman JP. Complex networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006;7:131–142. - PubMed
-
- Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139:871–890. - PubMed
-
- Chapman HA. Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in pulmonary fibrosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2011;73:413–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

