Human β-cell proliferation and intracellular signaling part 2: still driving in the dark without a road map
- PMID: 24556859
- PMCID: PMC3931400
- DOI: 10.2337/db13-1146
Human β-cell proliferation and intracellular signaling part 2: still driving in the dark without a road map
Abstract
Enhancing β-cell proliferation is a major goal for type 1 and type 2 diabetes research. Unraveling the network of β-cell intracellular signaling pathways that promote β-cell replication can provide the tools to address this important task. In a previous Perspectives in Diabetes article, we discussed what was known regarding several important intracellular signaling pathways in rodent β-cells, including the insulin receptor substrate/phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt (IRS-PI3K-Akt) pathways, glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) S6 kinase pathways, protein kinase Cζ (PKCζ) pathways, and their downstream cell-cycle molecular targets, and contrasted that ample knowledge to the small amount of complementary data on human β-cell intracellular signaling pathways. In this Perspectives, we summarize additional important information on signaling pathways activated by nutrients, such as glucose; growth factors, such as epidermal growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and Wnt; and hormones, such as leptin, estrogen, and progesterone, that are linked to rodent and human β-cell proliferation. With these two Perspectives, we attempt to construct a brief summary of knowledge for β-cell researchers on mitogenic signaling pathways and to emphasize how little is known regarding intracellular events linked to human β-cell replication. This is a critical aspect in the long-term goal of expanding human β-cells for the prevention and/or cure of type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Figures

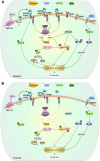

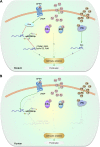
References
-
- Nakamura A, Terauchi Y, Ohyama S, et al. Impact of small-molecule glucokinase activator on glucose metabolism and beta-cell mass. Endocrinology 2009;150:1147–1154 - PubMed
-
- Guillam MT, Hümmler E, Schaerer E, et al. Early diabetes and abnormal postnatal pancreatic islet development in mice lacking Glut-2 [published correction appears in Nat Genet 1997;17:503]. Nat Genet 1997;17:327–330 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK074970/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK073716/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK069362/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK67351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK55023/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD044405/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- HD044405/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK77096/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK065149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055023/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK074970/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK065149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK055523/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK067536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK067536/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK069362/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067351/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK084236/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK073716/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK077096/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK084236/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK089538/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK065149/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK055523/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

