NTCP and beyond: opening the door to unveil hepatitis B virus entry
- PMID: 24557582
- PMCID: PMC3958888
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15022892
NTCP and beyond: opening the door to unveil hepatitis B virus entry
Abstract
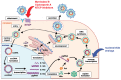
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, affecting approximately 240 million people worldwide, is a major public health problem that elevates the risk of developing liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Given that current anti-HBV drugs are limited to interferon-based regimens and nucleos(t)ide analogs, the development of new anti-HBV agents is urgently needed. The viral entry process is generally an attractive target implicated in antiviral strategies. Using primary cells from humans and Tupaia belangeri, as well as HepaRG cells, important determinants of viral entry have been achieved. Recently, sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide (NTCP) was identified as an HBV entry receptor and enabled the establishment of a susceptible cell line that can efficiently support HBV infection. This finding will allow a deeper understanding of the requirements for efficient HBV infection, including the elucidation of the molecular entry mechanism. In addition, pharmacological studies suggest that NTCP is able to serve as a therapeutic target. This article summarizes our current knowledge on the mechanisms of HBV entry and the role of NTCP in this process.
Figures
References
-
- Ott J.J., Stevens G.A., Groeger J., Wiersma S.T. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: New estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine. 2012;30:2212–2219. - PubMed
-
- Zoulim F., Locarnini S. Optimal management of chronic hepatitis B patients with treatment failure and antiviral drug resistance. Liver Int. 2013;33:116–124. - PubMed
-
- Zoulim F., Perrillo R., Hepatitis B. Reflections on the current approach to antiviral therapy. J. Hepatol. 2008;48:S2–S19. - PubMed
-
- Belloni L., Allweiss L., Guerrieri F., Pediconi N., Volz T., Pollicino T., Petersen J., Raimondo G., Dandri M., Levrero M. IFN-alpha inhibits HBV transcription and replication in cell culture and in humanized mice by targeting the epigenetic regulation of the nuclear cccDNA minichromosome. J. Clin. Invest. 2012;122:529–537. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources