Hippocampal volume is reduced in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder but not in psychotic bipolar I disorder demonstrated by both manual tracing and automated parcellation (FreeSurfer)
- PMID: 24557771
- PMCID: PMC4266285
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbu009
Hippocampal volume is reduced in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder but not in psychotic bipolar I disorder demonstrated by both manual tracing and automated parcellation (FreeSurfer)
Abstract
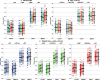
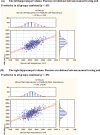
This study examined hippocampal volume as a putative biomarker for psychotic illness in the Bipolar-Schizophrenia Network on Intermediate Phenotypes (B-SNIP) psychosis sample, contrasting manual tracing and semiautomated (FreeSurfer) region-of-interest outcomes. The study sample (n = 596) included probands with schizophrenia (SZ, n = 71), schizoaffective disorder (SAD, n = 70), and psychotic bipolar I disorder (BDP, n = 86); their first-degree relatives (SZ-Rel, n = 74; SAD-Rel, n = 62; BDP-Rel, n = 88); and healthy controls (HC, n = 145). Hippocampal volumes were derived from 3Tesla T1-weighted MPRAGE images using manual tracing/3DSlicer3.6.3 and semiautomated parcellation/FreeSurfer5.1,64bit. Volumetric outcomes from both methodologies were contrasted in HC and probands and relatives across the 3 diagnoses, using mixed-effect regression models (SAS9.3 Proc MIXED); Pearson correlations between manual tracing and FreeSurfer outcomes were computed. SZ (P = .0007-.02) and SAD (P = .003-.14) had lower hippocampal volumes compared with HC, whereas BDP showed normal volumes bilaterally (P = .18-.55). All relative groups had hippocampal volumes not different from controls (P = .12-.97) and higher than those observed in probands (P = .003-.09), except for FreeSurfer measures in bipolar probands vs relatives (P = .64-.99). Outcomes from manual tracing and FreeSurfer showed direct, moderate to strong, correlations (r = .51-.73, P < .05). These findings from a large psychosis sample support decreased hippocampal volume as a putative biomarker for schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder, but not for psychotic bipolar I disorder, and may reflect a cumulative effect of divergent primary disease processes and/or lifetime medication use. Manual tracing and semiautomated parcellation regional volumetric approaches may provide useful outcomes for defining measurable biomarkers underlying severe mental illness.
Keywords: FreeSurfer; hippocampus; manual tracing; psychotic bipolar disorder; schizophrenia.
© The Author 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Altshuler LL, Bartzokis G, Grieder T, et al. An MRI study of temporal lobe structures in men with bipolar disorder or schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry. 2000;48:147–162. - PubMed
-
- Goldman AL, Pezawas L, Mattay VS, et al. Heritability of brain morphology related to schizophrenia: a large-scale automated magnetic resonance imaging segmentation study. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;63:475–483. - PubMed
-
- Nelson MD, Saykin AJ, Flashman LA, Riordan HJ. Hippocampal volume reduction in schizophrenia as assessed by magnetic resonance imaging: a meta-analytic study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1998;55:433–440. - PubMed
-
- Wright IC, Rabe-Hesketh S, Woodruff PW, David AS, Murray RM, Bullmore ET. Meta-analysis of regional brain volumes in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry. 2000;157:16–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

