Perfluoroalkyl substances during pregnancy and validated preeclampsia among nulliparous women in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study
- PMID: 24557813
- PMCID: PMC3969534
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/kwt432
Perfluoroalkyl substances during pregnancy and validated preeclampsia among nulliparous women in the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study
Abstract
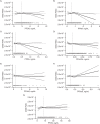
Perfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are persistent and ubiquitous environmental contaminants, and human exposure to these substances may be related to preeclampsia, a common pregnancy complication. Previous studies have found serum concentrations of PFAS to be positively associated with pregnancy-induced hypertension and preeclampsia in a population with high levels of exposure to perfluorooctanoate. Whether this association exists among pregnant women with background levels of PFAS exposure is unknown. Using data from the Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study conducted by the Norwegian Institute of Public Health, we carried out a study of nulliparous pregnant women enrolled in 2003-2007 (466 cases, 510 noncases) to estimate associations between PFAS concentrations and an independently validated diagnosis of preeclampsia. We measured levels of 9 PFAS in maternal plasma extracted midpregnancy; statistical analyses were restricted to 7 PFAS that were quantifiable in more than 50% of samples. In proportional hazards models adjusted for maternal age, prepregnancy body mass index (weight (kg)/height (m)(2)), educational level, and smoking status, we observed no strongly positive associations between PFAS levels and preeclampsia. We found an inverse association between preeclampsia and the highest quartile of perfluoroundecanoic acid concentration relative to the lowest quartile (hazard ratio = 0.55, 95% confidence interval: 0.38, 0.81). Overall, our findings do not support an increased risk of preeclampsia among nulliparous Norwegian women with background levels of PFAS exposure.
Keywords: Norwegian Mother and Child Cohort Study; perfluoroalkyl substances; perfluorooctane sulfonate; perfluorooctanoic acid; perfluoroundecanoic acid; preeclampsia.
Figures
References
-
- Wallis AB, Saftlas AF, Hsia J, et al. Secular trends in the rates of preeclampsia, eclampsia, and gestational hypertension, United States, 1987–2004. Am J Hypertens. 2008;21(5):521–526. - PubMed
-
- Klungsøyr K, Morken NH, Irgens L, et al. Secular trends in the epidemiology of pre-eclampsia throughout 40 years in Norway: prevalence, risk factors and perinatal survival. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2012;26(3):190–198. - PubMed
-
- Skjaerven R, Wilcox AJ, Lie RT. The interval between pregnancies and the risk of preeclampsia. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(1):33–38. - PubMed
-
- Hutcheon JA, Lisonkova S, Joseph KS. Epidemiology of pre-eclampsia and the other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;25(4):391–403. - PubMed
-
- Trogstad L, Magnus P, Stoltenberg C. Pre-eclampsia: risk factors and causal models. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2011;25(3):329–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

