Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA
- PMID: 24557838
- PMCID: PMC6309542
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1243462
Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA
Abstract
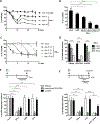
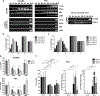
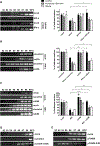
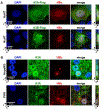
Current antiviral agents can control but not eliminate hepatitis B virus (HBV), because HBV establishes a stable nuclear covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA). Interferon-α treatment can clear HBV but is limited by systemic side effects. We describe how interferon-α can induce specific degradation of the nuclear viral DNA without hepatotoxicity and propose lymphotoxin-β receptor activation as a therapeutic alternative. Interferon-α and lymphotoxin-β receptor activation up-regulated APOBEC3A and APOBEC3B cytidine deaminases, respectively, in HBV-infected cells, primary hepatocytes, and human liver needle biopsies. HBV core protein mediated the interaction with nuclear cccDNA, resulting in cytidine deamination, apurinic/apyrimidinic site formation, and finally cccDNA degradation that prevented HBV reactivation. Genomic DNA was not affected. Thus, inducing nuclear deaminases-for example, by lymphotoxin-β receptor activation-allows the development of new therapeutics that, in combination with existing antivirals, may cure hepatitis B.
Figures

Comment in
-
Virology. Getting rid of a persistent troublemaker to cure hepatitis.Science. 2014 Mar 14;343(6176):1212-3. doi: 10.1126/science.1252186. Science. 2014. PMID: 24626921 No abstract available.
-
Virology. Comment on "Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA".Science. 2014 Jun 13;344(6189):1237. doi: 10.1126/science.1254082. Science. 2014. PMID: 24926010
-
Virology. Response to Comment on "Specific and nonhepatotoxic degradation of nuclear hepatitis B virus cccDNA".Science. 2014 Jun 13;344(6189):1237. doi: 10.1126/science.1254083. Science. 2014. PMID: 24926011
-
Cytidine deamination and cccDNA degradation: A new approach for curing HBV?Hepatology. 2014 Dec;60(6):2118-21. doi: 10.1002/hep.27386. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Hepatology. 2014. PMID: 25142126 No abstract available.
References
-
- Wursthorn K, Lutgehetmann M, Dandri M, Volz T, Buggisch P, Zollner B, Longerich T, Schirmacher P, Metzler F, Zankel M, Fischer C, Currie G, Brosgart C, Petersen J, Peginterferon alpha-2b plus adefovir induce strong cccDNA decline and HBsAg reduction in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 44, 675–684 (2006). doi:10.1002/hep.21282 Medline - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

