A nomogram for predicting distant brain failure in patients treated with gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery without whole brain radiotherapy
- PMID: 24558022
- PMCID: PMC4136890
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nou018
A nomogram for predicting distant brain failure in patients treated with gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery without whole brain radiotherapy
Abstract
Background: We review our single institution experience to determine predictive factors for early and delayed distant brain failure (DBF) after radiosurgery without whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) for brain metastases.
Materials and methods: Between January 2000 and December 2010, a total of 464 patients were treated with Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) without WBRT for primary management of newly diagnosed brain metastases. Histology, systemic disease, RPA class, and number of metastases were evaluated as possible predictors of DBF rate. DBF rates were determined by serial MRI. Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate rate of DBF. Multivariate analysis was performed using Cox Proportional Hazard regression.
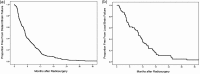
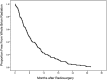
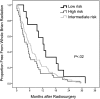
Results: Median number of lesions treated was 1 (range 1-13). Median time to DBF was 4.9 months. Twenty-seven percent of patients ultimately required WBRT with median time to WBRT of 5.6 months. Progressive systemic disease (χ(2)= 16.748, P < .001), number of metastases at SRS (χ(2) = 27.216, P < .001), discovery of new metastases at time of SRS (χ(2) = 9.197, P < .01), and histology (χ(2) = 12.819, P < .07) were factors that predicted for earlier time to distant failure. High risk histologic subtypes (melanoma, her2 negative breast, χ(2) = 11.020, P < .001) and low risk subtypes (her2 + breast, χ(2) = 11.343, P < .001) were identified. Progressive systemic disease (χ(2) = 9.549, P < .01), number of brain metastases (χ(2) = 16.953, P < .001), minimum SRS dose (χ(2) = 21.609, P < .001), and widespread metastatic disease (χ(2) = 29.396, P < .001) were predictive of shorter time to WBRT.
Conclusion: Systemic disease, number of metastases, and histology are factors that predict distant failure rate after primary radiosurgical management of brain metastases.
Keywords: brain metastases; distant brain failure; nomogram; stereotactic radiosurgery.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



References
-
- Niwinska A, Murawska M, Pogoda K. Breast cancer brain metastases: differences in survival depending on biological subtype, RPA RTOG prognostic class and systemic treatment after whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) Ann Oncol. 21(5):942–948. - PubMed
-
- Lin NU, Dieras V, Paul D, et al. Multicenter phase II study of lapatinib in patients with brain metastases from HER2-positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(4):1452–1459. - PubMed
-
- Nieder C, Leicht A, Motaref B, Nestle U, Niewald M, Schnabel K. Late radiation toxicity after whole brain radiotherapy: the influence of antiepileptic drugs. Am J Clin Oncol. 1999;22(6):573–579. - PubMed
-
- Sperduto PW, Chao ST, Sneed PK, et al. Diagnosis-specific prognostic factors, indexes, and treatment outcomes for patients with newly diagnosed brain metastases: a multi-institutional analysis of 4,259 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2010;77(3):655–661. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

