Adipose stem cells used to reconstruct 13 cases with cranio-maxillofacial hard-tissue defects
- PMID: 24558162
- PMCID: PMC3973720
- DOI: 10.5966/sctm.2013-0173
Adipose stem cells used to reconstruct 13 cases with cranio-maxillofacial hard-tissue defects
Abstract
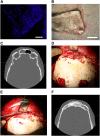
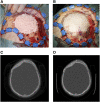
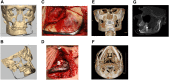
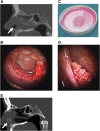
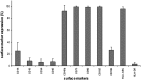
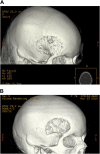
Although isolated reports of hard-tissue reconstruction in the cranio-maxillofacial skeleton exist, multipatient case series are lacking. This study aimed to review the experience with 13 consecutive cases of cranio-maxillofacial hard-tissue defects at four anatomically different sites, namely frontal sinus (3 cases), cranial bone (5 cases), mandible (3 cases), and nasal septum (2 cases). Autologous adipose tissue was harvested from the anterior abdominal wall, and adipose-derived stem cells were cultured, expanded, and then seeded onto resorbable scaffold materials for subsequent reimplantation into hard-tissue defects. The defects were reconstructed with either bioactive glass or β-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds seeded with adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs), and in some cases with the addition of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. Production and use of ASCs were done according to good manufacturing practice guidelines. Follow-up time ranged from 12 to 52 months. Successful integration of the construct to the surrounding skeleton was noted in 10 of the 13 cases. Two cranial defect cases in which nonrigid resorbable containment meshes were used sustained bone resorption to the point that they required the procedure to be redone. One septal perforation case failed outright at 1 year because of the postsurgical resumption of the patient's uncontrolled nasal picking habit.
Keywords: Adipose stem cells; Bioactive glass; Bone morphogenetic protein; β-Tricalcium phosphate.
Figures
References
-
- Bianchi B, Ferri A, Ferrari S, et al. Mandibular resection and reconstruction in the management of extensive ameloblastoma. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71:528–537. - PubMed
-
- Hidalgo DA. Fibula free flap: A new method of mandible reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1989;84:71–79. - PubMed
-
- Sàndor GK, Nish IA, Carmichael RP. Comparison of conventional surgery with motorized trephine in bone harvest from the anterior iliac crest. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003;95:150–155. - PubMed
-
- Ling XF, Peng X. What is the price to pay for a free fibula flap? A systematic review of donor-site morbidity following free fibula flap surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129:657–674. - PubMed
-
- Sieg P, Taner C, Hakim SG, et al. Long-term evaluation of donor site morbidity after free fibula transfer. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;48:267–270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

