Complete dosage compensation and sex-biased gene expression in the moth Manduca sexta
- PMID: 24558255
- PMCID: PMC3971586
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evu035
Complete dosage compensation and sex-biased gene expression in the moth Manduca sexta
Abstract
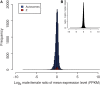
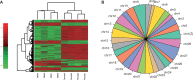
Sex chromosome dosage compensation balances homogametic sex chromosome expression with autosomal expression in the heterogametic sex, leading to sex chromosome expression parity between the sexes. If compensation is incomplete, this can lead to expression imbalance and sex-biased gene expression. Recent work has uncovered an intriguing and variable pattern of dosage compensation across species that includes a lack of complete dosage compensation in ZW species compared with XY species. This has led to the hypothesis that ZW species do not require complete compensation or that complete compensation would negatively affect their fitness. To date, only one study, a study of the moth Bombyx mori, has discovered evidence for complete dosage compensation in a ZW species. We examined another moth species, Manduca sexta, using high-throughput sequencing to survey gene expression in the head tissue of males and females. We found dosage compensation to be complete in M. sexta with average expression between the Z chromosome in males and females being equal. When genes expressed at very low levels are removed by filtering, we found that average autosome expression was highly similar to average Z expression, suggesting that the majority of genes in M. sexta are completely dosage compensated. Further, this compensation was accompanied by sex-specific gene expression associated with important sexually dimorphic traits. We suggest that complete dosage compensation in ZW species might be more common than previously appreciated and linked to additional selective processes, such as sexual selection. More ZW and lepidopteran species should now be examined in a phylogenetic framework, to understand the evolution of dosage compensation.
Keywords: Lepidoptera; dosage compensation; mushroom body; olfaction; phototransduction; sex-biased gene expression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Global Dosage Compensation Is Ubiquitous in Lepidoptera, but Counteracted by the Masculinization of the Z Chromosome.Mol Biol Evol. 2017 Oct 1;34(10):2637-2649. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx190. Mol Biol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28957502 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Chromosome Dosage Compensation in Heliconius Butterflies: Global yet Still Incomplete?Genome Biol Evol. 2015 Sep 2;7(9):2545-59. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv156. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 26338190 Free PMC article.
-
Conserved Patterns of Sex Chromosome Dosage Compensation in the Lepidoptera (WZ/ZZ): Insights from a Moth Neo-Z Chromosome.Genome Biol Evol. 2017 Mar 1;9(3):802-816. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evx039. Genome Biol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28338816 Free PMC article.
-
Dosage compensation of the sex chromosomes and autosomes.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016 Aug;56:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.04.013. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 27112542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex chromosome dosage compensation: definitely not for everyone.Trends Genet. 2013 Dec;29(12):677-83. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2013.07.005. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Trends Genet. 2013. PMID: 23953923 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of Phototransduction Genes in Lepidoptera.Genome Biol Evol. 2019 Aug 1;11(8):2107-2124. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evz150. Genome Biol Evol. 2019. PMID: 31298692 Free PMC article.
-
Global Dosage Compensation Is Ubiquitous in Lepidoptera, but Counteracted by the Masculinization of the Z Chromosome.Mol Biol Evol. 2017 Oct 1;34(10):2637-2649. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx190. Mol Biol Evol. 2017. PMID: 28957502 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of single-copy genes by TSA-FISH in the codling moth, Cydia pomonella.BMC Genet. 2014;15 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S15. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-15-S2-S15. Epub 2014 Dec 1. BMC Genet. 2014. PMID: 25471491 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial dynamics of evolving dosage compensation in a young sex chromosome system.Genome Biol Evol. 2015 Jan 23;7(2):581-90. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv013. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 25618140 Free PMC article.
-
Multifaceted biological insights from a draft genome sequence of the tobacco hornworm moth, Manduca sexta.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Sep;76:118-147. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27522922 Free PMC article.

