Liquid crystal assemblies in biologically inspired systems
- PMID: 24558293
- PMCID: PMC3927920
- DOI: 10.1080/02678292.2013.846422
Liquid crystal assemblies in biologically inspired systems
Abstract
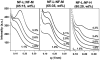
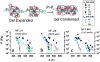
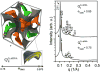
In this paper, which is part of a collection in honor of Noel Clark's remarkable career on liquid crystal and soft matter research, we present examples of biologically inspired systems, which form liquid crystal (LC) phases with their LC nature impacting biological function in cells or being important in biomedical applications. One area focuses on understanding network and bundle formation of cytoskeletal polyampholytes (filamentous-actin, microtubules, and neurofilaments). Here, we describe studies on neurofilaments (NFs), the intermediate filaments of neurons, which form open network nematic liquid crystal hydrogels in axons. Synchrotron small-angle-x-ray scattering studies of NF-protein dilution experiments and NF hydrogels subjected to osmotic stress show that neurofilament networks are stabilized by competing long-range repulsion and attractions mediated by the neurofilament's polyampholytic sidearms. The attractions are present both at very large interfilament spacings, in the weak sidearm-interpenetrating regime, and at smaller interfilament spacings, in the strong sidearm-interpenetrating regime. A second series of experiments will describe the structure and properties of cationic liposomes (CLs) complexed with nucleic acids (NAs). CL-NA complexes form liquid crystalline phases, which interact in a structure-dependent manner with cellular membranes enabling the design of complexes for efficient delivery of nucleic acid (DNA, RNA) in therapeutic applications.
Keywords: DNA; Neurofilaments; RNA; gyroid cubic phases; hexagonal liquid crystals; lamellar liquid crystals; lipids; nematic hydrogels; small-angle-x-ray-scattering (SAXS).
Figures

References
-
- Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM. Principles of Neural Science. 4th. McGraw Hill; New York: 2000.
-
- Peters A, Palay SL, Def H. The Fine Structure of the Nervous System. 3rd. Webster; New York: 1991.
-
- Burgoyne RD, editor. The Neuronal cytoskeleton. Wiley & Sons; New York: 1991.
-
- Hirokawa N. In: The Neuronal Cytoskeleton. Burgoyne RD, editor. Wiley; New York: 1991. pp. 5–74.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
