Effects of ginseol k-g3, an Rg3-enriched fraction, on scopolamine-induced memory impairment and learning deficit in mice
- PMID: 24558303
- PMCID: PMC3915335
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2013.11.003
Effects of ginseol k-g3, an Rg3-enriched fraction, on scopolamine-induced memory impairment and learning deficit in mice
Abstract
Background: Although ginsenosides such as Rg1, Rb1 and Rg3 have shown promise as potential nutraceuticals for cognitive impairment, their use has been limited due to high production cost and low potency. In particular, the process of extracting pure Rg3 from ginseng is laborious and expensive.
Methods: We described the methods in preparing ginseol k-g3, an Rg3-enriched fraction, and evaluated its effects on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice.
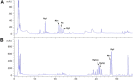
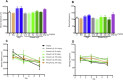
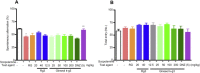
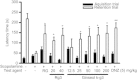
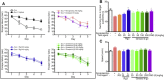
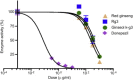
Results: Ginseol k-g3 (25-200 mg/kg) significantly reversed scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment in the passive avoidance, but not in Y-maze testing. Ginseol k-g3 (50 and 200 mg/kg) improved escape latency in training trials and increased swimming times within the target zone of the Morris water maze. The effect of ginseol k-g3 on the water maze task was more potent than that of Rg3 or Red ginseng. Acute or subchronic (6 d) treatment of ginseol k-g3 did not alter normal locomotor activity of mice in an open field. Ginseol k-g3 did not inhibit acetylcholinesterase activity, unlike donezepil, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Rg3 enrichment through the ginseol k-g3 fraction enhanced the efficacy of Rg3 in scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice as demonstrated in the Morris water maze task.
Conclusion: The effects of ginseol k-g3 in ameliorating scopolamine-induced memory impairment in the passive avoidance and Morris water maze tests indicate its specific influence on reference or long-term memory. The mechanism underlying the reversal of scopolamine-induced amnesia by ginseol k-g3 is not yet known, but is not related to anticholinesterase-like activity.
Keywords: Panax ginseng; Rg3; ginseol k-g3; memory; scopolamine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ginsenoside Rh2 ameliorates scopolamine-induced learning deficit in mice.Biol Pharm Bull. 2009 Oct;32(10):1710-5. doi: 10.1248/bpb.32.1710. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009. PMID: 19801832
-
Ginsenosides Rg5 and Rh3 protect scopolamine-induced memory deficits in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Mar 7;146(1):294-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.12.047. Epub 2013 Jan 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23313392
-
Rg3-enriched ginseng extract ameliorates scopolamine-induced learning deficits in mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Feb 18;16:66. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1050-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 26887326 Free PMC article.
-
Memory enhancing and neuroprotective effects of selected ginsenosides.Arch Pharm Res. 2005 Mar;28(3):335-42. doi: 10.1007/BF02977802. Arch Pharm Res. 2005. PMID: 15832823
-
Ginsenosides Rg5 and Rk1 Enriched Cultured Wild Ginseng Root Extract Bioconversion of Pediococcus pentosaceus HLJG0702: Effect on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Dysfunction in Mice.Nutrients. 2019 May 20;11(5):1120. doi: 10.3390/nu11051120. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31137483 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ginseng berry aqueous extract prevents scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Dec;18(6):4388-4396. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.8090. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31772634 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Methanolic Extract of Vitellaria paradoxa Stem Bark Against Scopolamine-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in the Rat Hippocampus.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Oct;36(7):1139-49. doi: 10.1007/s10571-015-0310-7. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26620052 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Derivatives of diphenyl-1,3,4-oxadiazol as Ligands of Benzodiazepine Receptors; Synthesize, Binding Assay and Pharmacological Evaluation.Iran J Pharm Res. 2021 Fall;20(4):47-58. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2021.115549.15429. Iran J Pharm Res. 2021. PMID: 35194427 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Anticonvulsant Effect of Aqueous and Methanolic Extracts of Seven Inula Species.Iran J Pharm Res. 2019 Fall;18(Suppl1):208-220. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.15509.13151. Iran J Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 32802101 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective and Antiamnesic Effects of Mitragyna inermis Willd (Rubiaceae) on Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment in Mice.Behav Neurol. 2017;2017:5952897. doi: 10.1155/2017/5952897. Epub 2017 Mar 12. Behav Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28386162 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Terry R.D. The fine structure of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1963;22:629–642. - PubMed
-
- Braak H., Braak E. Frequency of stages of Alzheimer-related lesions in different age categories. Neurobiol Aging. 1997;18:351–357. - PubMed
-
- Bartus R.T., Dean R.L., 3rd, Beer B., Lippa A. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science. 1982;217:408–417. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

