Metabolomic approach for discrimination of processed ginseng genus (Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius) using UPLC-QTOF MS
- PMID: 24558312
- PMCID: PMC3915342
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2013.11.011
Metabolomic approach for discrimination of processed ginseng genus (Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius) using UPLC-QTOF MS
Abstract
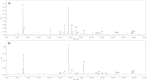
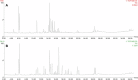
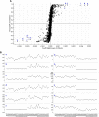
Discriminating between two herbal medicines (Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius), with similar chemical and physical properties but different therapeutic effects, is a very serious and difficult problem. Differentiation between two processed ginseng genera is even more difficult because the characteristics of their appearance are very similar. An ultraperformance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF MS)-based metabolomic technique was applied for the metabolite profiling of 40 processed P. ginseng and processed P. quinquefolius. Currently known biomarkers such as ginsenoside Rf and F11 have been used for the analysis using the UPLC-photodiode array detector. However, this method was not able to fully discriminate between the two processed ginseng genera. Thus, an optimized UPLC-QTOF-based metabolic profiling method was adapted for the analysis and evaluation of two processed ginseng genera. As a result, all known biomarkers were identified by the proposed metabolomics, and additional potential biomarkers were extracted from the huge amounts of global analysis data. Therefore, it is expected that such metabolomics techniques would be widely applied to the ginseng research field.
Keywords: Panax ginseng; Panax quinquefolius; UPLC-QTOF MS; discrimination; metabolomics.
Figures

References
-
- Soldati F. Panax ginseng; standardization and biological activity. In: Cutler S.J., Cutler H.G., editors. Biologically active natural products. CRC Press; New York: 2000. pp. 209–232.
-
- Chan T.W.D., But P.P.H., Cheng S.W., Kwok I.M.Y., Lau F.W., Xu H.X. Differentiation and authentication of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius, and ginseng products by using HPLC/MS. Anal Chem. 2000;72:1281–1287. - PubMed
-
- Leung Kelvin S.Y., Chan K., Bensoussan A., Munroe M.J. Application of atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry in the identification and differentiation of Panax species. Phytochem Anal. 2007;18:146–150. - PubMed
-
- Li L., Luo G.A., Liang Q.L., Hu P., Wang Y.M. Rapid qualitative and quantitative analyses of Asian ginseng in adulterated American ginseng preparations by UPLC/Q-TOF-MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2010;52:66–72. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

