Ginsenoside profiles and related gene expression during foliation in Panax ginseng Meyer
- PMID: 24558313
- PMCID: PMC3915334
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2013.11.001
Ginsenoside profiles and related gene expression during foliation in Panax ginseng Meyer
Abstract
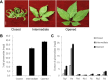
Panax ginseng is one of the most important medicinal plants in Asia. Triterpene saponins, known as ginsenosides, are the major pharmacological compounds in P. ginseng. The present study was conducted to evaluate the changes in ginsenoside composition according to the foliation stage of P. ginseng cultured in a hydroponic system. Among the three tested growth stages (closed, intermediate, and opened), the highest amount of total ginsenoside in the main and fine roots was in the intermediate stage. In the leaves, the highest amount of total ginsenoside was in the opened stage. The total ginsenoside content of the ginseng leaf was markedly increased in the transition from the closed to intermediate stage, and increased more slowly from the intermediate to opened leaf stage, suggesting active biosynthesis of ginsenosides in the leaf. Conversely, the total ginsenoside content of the main and fine roots decreased from the intermediate to opened leaf stage. This suggests movement of ginsenosides during foliation from the root to the leaf, or vice versa. The difference in the composition of ginsenosides between the leaf and root in each stage of foliation suggests that the ginsenoside profile is affected by foliation stage, and this profile differs in each organ of the plant. These results suggest that protopanaxadiol- and protopanaxatriol (PPT)-type ginsenosides are produced according to growth stage to meet different needs in the growth and defense of ginseng. The higher content of PPT-type ginsenosides in leaves could be related to the positive correlation between light and PPT-type ginsenosides.
Keywords: HPLC; Panax ginseng; foliation stage; ginsenoside; hydroponics.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modification of ginsenoside saponin composition via the CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout of protopanaxadiol 6-hydroxylase gene in Panax ginseng.J Ginseng Res. 2022 Jul;46(4):505-514. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2021.06.004. Epub 2021 Jun 18. J Ginseng Res. 2022. PMID: 35818421 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of ginsenosides in different tissues after elicitor treatment in Panax ginseng.J Ginseng Res. 2014 Oct 15;38(4):270-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2014.04.004. Epub 2014 May 23. J Ginseng Res. 2014. PMID: 25379007 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Ginsenoside Contents in Different Parts of Korean Ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer).Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2016 Dec;21(4):389-392. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2016.21.4.389. Epub 2016 Dec 31. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2016. PMID: 28078264 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Saponin Diversity of Panax ginseng.Molecules. 2020 Jul 29;25(15):3452. doi: 10.3390/molecules25153452. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32751233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research achievements on ginsenosides biosynthesis from Panax ginseng].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Dec;41(23):4292-4302. doi: 10.4268/cjcmm20162302. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28933103 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Subtractive transcriptome analysis of leaf and rhizome reveals differentially expressed transcripts in Panax sokpayensis.Funct Integr Genomics. 2016 Nov;16(6):619-639. doi: 10.1007/s10142-016-0517-9. Epub 2016 Sep 1. Funct Integr Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27586658
-
Quantitative Analyses of the Functional Constituents in SanYangSam and SanYangSanSam.J Pharmacopuncture. 2017 Dec;20(4):274-279. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2017.20.033. Epub 2017 Oct 11. J Pharmacopuncture. 2017. PMID: 30151297 Free PMC article.
-
Rare ginsenoside Ia synthesized from F1 by cloning and overexpression of the UDP-glycosyltransferase gene from Bacillus subtilis: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro melanogenesis inhibition activity in BL6B16 cells.J Ginseng Res. 2018 Jan;42(1):42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2016.12.009. Epub 2016 Dec 24. J Ginseng Res. 2018. PMID: 29348721 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive comparative analysis of chloroplast genomes from seven Panax species and development of an authentication system based on species-unique single nucleotide polymorphism markers.J Ginseng Res. 2020 Jan;44(1):135-144. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2018.06.003. Epub 2018 Jun 22. J Ginseng Res. 2020. PMID: 32148396 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Korean Red Ginseng Compound Gintonin Inhibited Inflammation by MAPK and NF-κB Pathways and Recovered the Levels of mir-34a and mir-93 in RAW 264.7 Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:624132. doi: 10.1155/2015/624132. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26579204 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Radad K., Gille G., Liu L., Rausch W.D. Use of ginseng in medicine with emphasis on neurodegenerative disorders. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006;100:175–186. - PubMed
-
- Attele A.S., Wu J.A., Yuan C.S. Ginseng pharmacology: multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999;58:1685–1693. - PubMed
-
- Im K.S., Chung H.Y., Park S.H., Je N.K. Anticancer effect of the hydrolyzed monogluco-ginsenoside of total saponin from ginseng leaf. Korean J Ginseng Sci. 1995;19:291–294.
-
- Li X., Wan H.G., Lu D.Q., Wei P. Advance of research on antitumour activity of ginsenosides. Chin J Bioprocess Eng. 2003;1:13–17.
-
- Xie J.T., Mehendale S.R., Li X., Quigg R., Wang X., Wang C.Z., Wu J.A., Aung H.H., A Rue P., Bell G.I. Anti-diabetic effect of ginsenoside Re in ob/ob mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005;1740:319–325. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

