Identification and characterization of sebaceous gland atrophy-sparing DGAT1 inhibitors
- PMID: 24558447
- PMCID: PMC3928314
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088908
Identification and characterization of sebaceous gland atrophy-sparing DGAT1 inhibitors
Abstract
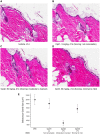
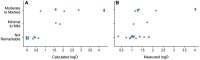
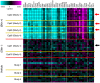
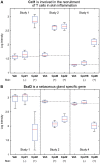
Inhibition of Diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) has been a mechanism of interest for metabolic disorders. DGAT1 inhibition has been shown to be a key regulator in an array of metabolic pathways; however, based on the DGAT1 KO mouse phenotype the anticipation is that pharmacological inhibition of DGAT1 could potentially lead to skin related adverse effects. One of the aims in developing small molecule DGAT1 inhibitors that target key metabolic tissues is to avoid activity on skin-localized DGAT1 enzyme. In this report we describe a modeling-based approach to identify molecules with physical properties leading to differential exposure distribution. In addition, we demonstrate histological and RNA based biomarker approaches that can detect sebaceous gland atrophy pre-clinically that could be used as potential biomarkers in a clinical setting.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Turkish A, Sturley SL (2007) Regulation of triglyceride metabolism. I. Eukaryotic neutral lipid synthesis: “Many ways to skin ACAT or a DGAT”. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 292: G953–957. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Gorski JN, Gold SJ, Chen D, Chen S, et al. (2013) Pharmacological inhibition of diacylglycerol acyltransferase 1 reduces body weight and modulates gut peptide release-Potential insight into mechanism of action. Obesity (Silver Spring). 21: 1406–1415. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

