Copper/TEMPO-Catalyzed Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation: Mechanistic Assessment of Different Catalyst Systems
- PMID: 24558634
- PMCID: PMC3925889
- DOI: 10.1021/cs400689a
Copper/TEMPO-Catalyzed Aerobic Alcohol Oxidation: Mechanistic Assessment of Different Catalyst Systems
Abstract
Combinations of homogeneous Cu salts and TEMPO have emerged as practical and efficient catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of alcohols. Several closely related catalyst systems have been reported, which differ in the identity of the solvent, the presence of 2,2'-bipyridine as a ligand, the identity of basic additives, and the oxidation state of the Cu source. These changes have a significant influence on the reaction rates, yields, and substrate scope. In this report, we probe the mechanistic basis for differences among four different Cu/TEMPO catalyst systems and elucidate the features that contribute to efficient oxidation of aliphatic alcohols.
Keywords: TEMPO; aerobic; alcohol oxidation; copper; kinetics; mechanism.
Figures
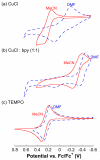
 ) and without (
) and without ( ) bpy in DMF. Standard conditions: 0.4 M CyCH2OH, 0.04 M TEMPO, 0.04 M CuCl, 0.04 M bpy, 600 torr O2, 27 °C.
) bpy in DMF. Standard conditions: 0.4 M CyCH2OH, 0.04 M TEMPO, 0.04 M CuCl, 0.04 M bpy, 600 torr O2, 27 °C.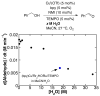
 ) included for comparison.
) included for comparison.
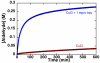
 ) and [(bpy)Cu(OH)]2(OTf)2. (
) and [(bpy)Cu(OH)]2(OTf)2. ( ). Data were obtained by monitoring pressure changes during catalytic turnover. Reaction conditions: 10 mM (bpy)Cu, 10 mM TEMPO, 20 mM NMI: 0.2 M CyCH2 OH, 1 atm O2, 2.5 mL MeCN, 27 °C.
). Data were obtained by monitoring pressure changes during catalytic turnover. Reaction conditions: 10 mM (bpy)Cu, 10 mM TEMPO, 20 mM NMI: 0.2 M CyCH2 OH, 1 atm O2, 2.5 mL MeCN, 27 °C.
 ) is included in A for comparison. Rates were obtained by monitoring pressure changes during catalytic turnover. Standard reaction conditions: 10 mM CuI(OTf), 10 mM bpy, 20 mM NMI, 10 mM TEMPO, 0.2 M alcohol.
) is included in A for comparison. Rates were obtained by monitoring pressure changes during catalytic turnover. Standard reaction conditions: 10 mM CuI(OTf), 10 mM bpy, 20 mM NMI, 10 mM TEMPO, 0.2 M alcohol.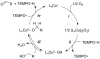

References
-
- Tojo G, Fernández M. In: Oxidation of Alcohols to Aldehydes and Ketones. Tojo G, editor. Springer; New York: 2010.
-
- Arends IWCE, Sheldon RA. In: Modern Oxidation Methods. Bäckvall J-E, editor. Wiley-VCH Verlag Gmb & Co.; Weinheim: 2004. pp. 83–118.
- Sheldon RA, Arends IWCE, ten Brink G-J, Dijksman A. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002;35:774–781. - PubMed
- Zhan BZ, Thompson A. Tetrahedron. 2004;60:2917–2935.
- Mallat T, Baiker A. Chem. Rev. 2004;104:3037–3058. - PubMed
- Stahl SS. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2004;43:3400–3420. - PubMed
- Markó IE, Giles PR, Tsukazaki M, Chellé-Regnaut I, Gautier A, Dumeunier R, Philippart F, Doda K, Mutonkole J-L, Brown SM, Urch CJ. Adv. Inorg. Chem. 2004;56:211–240.
- Schultz MJ, Sigman MS. Tetrahedron. 2006;62:8227–8241.
- Sigman MS, Jensen DR. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006;39:221–229. - PubMed
- Karimi B, Zamani A. J Iran Chem Soc. 2008;5:S1–S20.
- Matsumoto T, Ueno M, Wang N, Kobayashi S. Chem-Asian J. 2008;3:196–214. - PubMed
- Parmeggiani C, Cardona F. Green Chem. 2012;14:547–564.
-
- Semmelhack MF, Schmid CR, Cortés DA, Chou CS. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1984;106:3374–3376.
-
- Gamez P, Arends IWCE, Reedijk J, Sheldon RA. Chem. Commun. 2003:2414–2415. - PubMed
- Gamez P, Arends IWCE, Sheldon RA, Reedijk J. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004;346:805–811.
-
- Kumpulainen ETT, Koskinen AMP. Chem. Eur. J. 2009;15:10901–10911. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
