Differences in virulence of pneumolysin and autolysin mutants constructed by insertion duplication mutagenesis and in-frame deletion in Streptococcus pneumoniae
- PMID: 24558977
- PMCID: PMC3936844
- DOI: 10.1186/1472-6750-14-16
Differences in virulence of pneumolysin and autolysin mutants constructed by insertion duplication mutagenesis and in-frame deletion in Streptococcus pneumoniae
Abstract
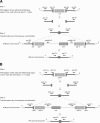
Background: Insertion duplication mutagenesis (IDM) and in-frame deletion (IFD) are common techniques for studying gene function, and have been applied to pneumolysin (ply), a virulence gene in Streptococcus pneumoniae (D39). Discrepancies in virulence between the two techniques were observed in both the previous and present studies. This phenomenon was also observed during mutation analysis of autolysin (lytA).
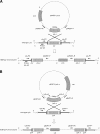
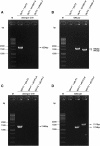
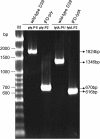
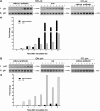
Results: Our data showed that target gene restoration (TGR) occurred in IDM mutants, even in the presence of antibiotics, while the IFD mutants were stable. In PCR result, TGR occurred later in IDM-ply and -lytA mutants cultured in non-supplemented medium (4-5 h) compared with those grown in medium supplemented with erythromycin (erm)/chloramphenicol (cat) (3-4 h), but plateaued faster. Real-time PCR for detecting TGR had been performed. When compared with 8-h culture, TGR detection increased from Day 1 and Day 2 of IDM mutant's culture. erm-sensitive clones from IDM mutant were found. Southern blot hybridization and Western blotting also confirmed the phenomenon of TGR. The median survival of mice following intraperitoneal (IP) injection with a 3-h culture of IDM-mutants was significantly longer than that with an 8-h culture, irrespective of antibiotic usage. The median survival time of mice following IP injection of a 3-h culture versus an 8-h culture of IDM-ply in the absence of antibiotics was 10 days versus 2 days (p = 0.031), respectively, while in the presence of erm, the median survival was 5 days versus 2.5 days (p = 0.037), respectively. For an IDM-lytA mutant, the corresponding values were 8.5 days versus 2 days (p = 0.019), respectively, for non-supplemented medium, and 2.5 versus 2 days (p = 0.021), respectively, in the presence of cat. A comparable survival rate was observed between WT D39 and an 8-h IDM culture.
Conclusion: TGR in IDM mutants should be monitored to avoid inconsistent results, and misinterpretation of data due to TGR could lead to important biological meaning being overlooked. Therefore, based on these results, IFD is preferable to IDM for disruption of target genes.
Figures
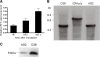
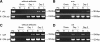
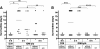
Similar articles
-
Additive attenuation of virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae by mutation of the genes encoding pneumolysin and other putative pneumococcal virulence proteins.Infect Immun. 2000 Jan;68(1):133-40. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.1.133-140.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10603379 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of insertional inactivation of the genes encoding pneumolysin and autolysin on the virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae type 3.Microb Pathog. 1992 Feb;12(2):87-93. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(92)90111-z. Microb Pathog. 1992. PMID: 1350046
-
Naturally-occurring serotype 3 Streptococcus pneumoniae strains that lack functional pneumolysin and autolysin have attenuated virulence but induce localized protective immune responses.PLoS One. 2023 Mar 10;18(3):e0282843. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282843. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36897919 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of pneumolysin and autolysin genes among antibiotic resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in invasive infections.Indian J Med Microbiol. 2010 Jan-Mar;28(1):34-9. doi: 10.4103/0255-0857.58726. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20061761
-
Molecular and cellular biology of pneumococcal infection.Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999 Feb;2(1):35-9. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(99)80006-x. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10047549 Review.
Cited by
-
Detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b, Streptococcus agalactiae, Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis in CSF specimens of children suspicious of Meningitis in Ahvaz, Iran.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2016 Oct;32(10):501-506. doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2016.08.009. Epub 2016 Sep 30. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27742033 Free PMC article.
-
Co-infection with dual Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes as a cause of pediatric bacterial meningitis in Iran: a multi-center cross-sectional study.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Jul 18;22(1):625. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07606-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35850636 Free PMC article.
-
Recombineering in Streptococcus mutans Using Direct Repeat-Mediated Cloning-Independent Markerless Mutagenesis (DR-CIMM).Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 May 23;7:202. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00202. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28589101 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

