Prognostic significance of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 24559042
- PMCID: PMC4015698
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-117
Prognostic significance of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Backgrounds: Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has recently been reported as a predictor of Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, its prognostic value in HCC still remains controversial. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the association between NLR and clinical outcome of HCC patients by performing meta-analysis.
Methods: A comprehensive literature search for relevant studies published up to August 2013 was performed by using PubMed, Ovid, the Cochrane Library and Web of Science databases. Meta-analysis was performed using hazard ratio (HR) or odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) as effect measures.
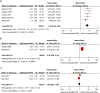
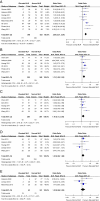
Results: A total of 15 studies encompassing 3094 patients were included in this meta-analysis. Our pooled results showed that high NLR was associated with poor overall survival (OS) and disease free survival (DFS) in HCC initially treated by liver transplantation (HR = 3.42, 95% CI:2.41-4.85,P = 0.000; HR = 5.90, 95% CI:3.99-8.70,P = 0.000, respectively) and surgical resection (HR = 3.33, 95% CI:2.23-4.98, P = 0.000; HR = 2.10, 95% CI: 2.06-2.14, respectively). High NLR was also associated with poor OS in HCC treated by radiofrequency-ablation (HR = 1.28, 95%CI: 1.10-1.48, P = 0.000), TACE (HR = 2.52, 95% CI: 1.64-3.86, P = 0.000) and mixed treatment (HR = 1.85, 95% CI: 1.40-2.44, P = 0.000), respectively. In addition, high NLR was significantly correlated with the presence of vascular invasion (OR = 2.69, 95% CI: 2.01-3.59, P = 0.000), tumor multifocality (OR = 1.74, 95% CI: 1.30-2.34, P = 0.000) and higher incidence of AFP ≥ 400 ng/ml (OR = 1.46, 95% CI: 1.01-2.09, P = 0.04).
Conclusion: Elevated NLR indicates a poor prognosis for patients with HCC. NLR may be a convenient, easily-obtained, low cost and reliable biomarker with prognostic potential for HCC.
Figures

References
-
- Proctor MJ, Talwar D, Balmar SM, O'Reilly DS, Foulis AK, Horgan PG, Morrison DS, McMillan DC. The relationship between the presence and site of cancer, an inflammation-based prognostic score and biochemical parameters. Initial results of the Glasgow Inflammation Outcome Study. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:870–876. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605855. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Szkandera J, Gerger A, Liegl-Atzwanger B, Absenger G, Stotz M, Samonigg H, Maurer-Ertl W, Stojakovic T, Ploner F, Leithner A, Pichler M. Validation of the prognostic relevance of plasma C-reactive protein levels in soft-tissue sarcoma patients. Br J Cancer. 2013;109:2316–2322. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2013.595. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

