Procalcitonin as a marker of Candida species detection by blood culture and polymerase chain reaction in septic patients
- PMID: 24559080
- PMCID: PMC3936855
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2253-14-9
Procalcitonin as a marker of Candida species detection by blood culture and polymerase chain reaction in septic patients
Abstract
Background: The aim of our study is to test procalcitonin (PCT) as surrogate marker of identification of Candida spp. by blood culture (BC) and real-time-polymerase chain reaction (PCR), whether alone or in association with bacteria, in septic patients.
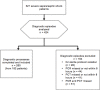
Methods: We performed a single-centre retrospective study. We reviewed the clinical charts of patients with a diagnosis of severe sepsis or septic shock treated at our general intensive care unit from March 2009 to March 2013. We analysed all diagnostic episodes consisting of BC, real-time PCR assay and dosage of PCT. We registered age, sex, white blood count, sequential organ failure assessment score and type of admission between medical or surgical. When inclusion criteria were met more than once, we registered the new diagnostic episode as subsequent diagnostic episode. The diagnostic performance of PCT to predict Candida spp. identification alone or in mixed infections by either BC or PCR was tested using the receiver-operative characteristic curve. Logistic regression was constructed using presence of Candida spp. as the dependent variable.
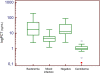
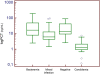
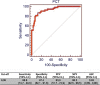
Results: A total of 260 diagnostic episodes met the inclusion criteria. According to BC results classification, a significantly lower value of PCT was observed in Candida spp. BSI (0.99 ng/ml, 0.86 - 1.34) than in BSI caused by bacteria (16.7 ng/ml, 7.65 - 50.2) or in mixed infections (4.76 ng/ml, 2.98 - 6.08). Similar findings were observed considering PCR results. A cut-off of ≤ 6.08 ng/ml for PCT yielded a sensitivity of 86.8%, a specificity of 87.4%, a positive predictive value of 63.9%, a negative predictive value (NPV) of 96.3% and an area under the curve of 0.93 for Candida spp. identification by BC. A similar high NPV for a cut-off ≤ 6.78 ng/ml was observed considering the classification of diagnostic episodes according to PCR results, with an AUC of 0.85. A subsequent diagnostic episode was independently associated with Candida spp. detection either by BC or PCR.
Conclusion: PCT could represent a useful diagnostic tool to exclude the detection of Candida spp. by BC and PCR in septic patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Procalcitonin is a marker of gram-negative bacteremia in patients with sepsis.Am J Med Sci. 2015 Jun;349(6):499-504. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0000000000000477. Am J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25992537 Free PMC article.
-
Procalcitonin predicts real-time PCR results in blood samples from patients with suspected sepsis.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e53279. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053279. Epub 2012 Dec 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300907 Free PMC article.
-
[The value of pro-adrenomedullin in early diagnosis of sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015 Sep;27(9):739-42. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2015. PMID: 26955700 Chinese.
-
The influence of sepsis on erythrocytes morphology: case report and literature review.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2024 Jan-Mar;65(1):119-123. doi: 10.47162/RJME.65.1.15. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2024. PMID: 38527992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Detection, Diagnosis, Prevention, and Treatment of Infection to Avoid Sepsis and Septic Shock in Severely Burned Patients: A Narrative Review.Eur Burn J. 2025 Feb 6;6(1):6. doi: 10.3390/ebj6010006. Eur Burn J. 2025. PMID: 39982339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Procalcitonin is a marker of gram-negative bacteremia in patients with sepsis.Am J Med Sci. 2015 Jun;349(6):499-504. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0000000000000477. Am J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25992537 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid molecular assays versus blood culture for bloodstream infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis.EClinicalMedicine. 2025 Jan 10;79:103028. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103028. eCollection 2025 Jan. EClinicalMedicine. 2025. PMID: 39968206 Free PMC article.
-
Ability of serum procalcitonin to distinguish focus of infection and pathogen types in patients with bloodstream infection.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Apr;7(7):135. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.03.24. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31157256 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of blood procalcitonin concentration in the management of cancer patients with infections.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Jan 22;9:469-75. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S95600. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 26858528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Procalcitonin for Predicting Blood Culture Results in Patients With Suspected Bloodstream Infection: An Observational Study of 35,343 Consecutive Patients (A STROBE-Compliant Article).Medicine (Baltimore). 2015 Nov;94(44):e1774. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001774. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015. PMID: 26554775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morrell M, Fraser VJ, Kollef MH. Delaying the empiric treatment of Candida bloodstream infection until positive blood culture results are obtained: a potential risk factor for hospital mortality. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49(9):3640–3645. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.9.3640-3645.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

