Reduced C9orf72 protein levels in frontal cortex of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal degeneration brain with the C9ORF72 hexanucleotide repeat expansion
- PMID: 24559645
- PMCID: PMC3988882
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.01.016
Reduced C9orf72 protein levels in frontal cortex of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal degeneration brain with the C9ORF72 hexanucleotide repeat expansion
Abstract
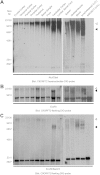
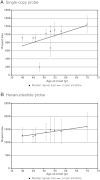
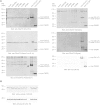
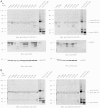
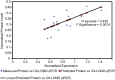
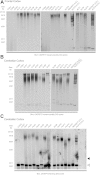
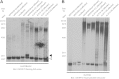
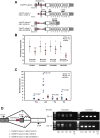
An intronic G(4)C(2) hexanucleotide repeat expansion in C9ORF72 is a major cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Several mechanisms including RNA toxicity, repeat-associated non-AUG translation mediated dipeptide protein aggregates, and haploinsufficiency of C9orf72 have been implicated in the molecular pathogenesis of this disorder. The aims of this study were to compare the use of two different Southern blot probes for detection of repeat expansions in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration pathological cohort and to determine the levels of C9orf72 transcript variants and protein isoforms in patients versus control subjects. Our Southern blot studies identified smaller repeat expansions (250-1800 bp) that were only detectable with the flanking probe highlighting the potential for divergent results using different Southern blotting protocols that could complicate genotype-phenotype correlation studies. Further, we characterize a new C9orf72 antibody and show for the first time decreased C9orf72 protein levels in the frontal cortex from patients with a pathological hexanucleotide repeat expansion. These data suggest that a reduction in C9orf72 protein may be a consequence of the disease.
Keywords: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; C9orf72; Frontotemporal dementia; Frontotemporal lobar degeneration; Repeat expansion; Southern blotting.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Almeida S., Gascon E., Tran H., Chou H.J., Gendron T.F., Degroot S., Tapper A.R., Sellier C., Charlet-Berguerand N., Karydas A., Seeley W.W., Boxer A.L., Petrucelli L., Miller B.L., Gao F.B. Modeling key pathological features of frontotemporal dementia with C9ORF72 repeat expansion in iPSC-derived human neurons. Acta Neuropathol. 2013 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ash P.E., Bieniek K.F., Gendron T.F., Caulfield T., Lin W.L., Dejesus-Hernandez M., van Blitterswijk M.M., Jansen-West K., Paul J.W., 3rd, Rademakers R., Boylan K.B., Dickson D.W., Petrucelli L. Unconventional translation of C9ORF72 GGGGCC expansion generates insoluble polypeptides specific to c9FTD/ALS. Neuron. 2013;77:639–646. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beck J., Poulter M., Hensman D., Rohrer J.D., Mahoney C.J., Adamson G., Campbell T., Uphill J., Borg A., Fratta P., Orrell R.W., Malaspina A., Rowe J., Brown J., Hodges J., Sidle K., Polke J.M., Houlden H., Schott J.M., Fox N.C., Rossor M.N., Tabrizi S.J., Isaacs A.M., Hardy J., Warren J.D., Collinge J., Mead S. Large C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansions are seen in multiple neurodegenerative syndromes and are more frequent than expected in the UK population. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013;92:345–353. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belzil V.V., Bauer P.O., Prudencio M., Gendron T.F., Stetler C.T., Yan I.K., Pregent L., Daughrity L., Baker M.C., Rademakers R., Boylan K., Patel T.C., Dickson D.W., Petrucelli L. Reduced C9orf72 gene expression in c9FTD/ALS is caused by histone trimethylation, an epigenetic event detectable in blood. Acta Neuropathol. 2013;126:895–905. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

