The many roles of PGC-1α in muscle--recent developments
- PMID: 24559845
- PMCID: PMC4040247
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metabol.2014.01.006
The many roles of PGC-1α in muscle--recent developments
Abstract
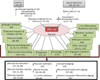
Skeletal muscle is the largest organ in the body and contributes to innumerable aspects of organismal biology. Muscle dysfunction engenders numerous diseases, including diabetes, cachexia, and sarcopenia. At the same time, skeletal muscle is also the main engine of exercise, one of the most efficacious interventions for prevention and treatment of a wide variety of diseases. The transcriptional coactivator PGC-1α has emerged as a key driver of metabolic programming in skeletal muscle, both in health and in disease. We review here the many aspects of PGC-1α function in skeletal muscle, with a focus on recent developments.
Keywords: Metabolism; Muscle; PGC-1alpha.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Puigserver P, Wu Z, Park CW, et al. A Cold-Inducible Coactivator of Nuclear Receptors Linked to Adaptive Thermogenesis. Cell. 1998;92(6):829–839. - PubMed
-
- Wu Z, Puigserver P, Ansersson, et al. Mechanisms Controlling Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Respiration through the Thermogenic Coactivator PGC-1α. Cell. 1999;98(1):115–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

