Scaling relationship and optimization of double-pulse electroporation
- PMID: 24559983
- PMCID: PMC3944924
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.12.045
Scaling relationship and optimization of double-pulse electroporation
Abstract
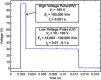
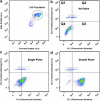
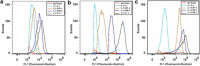
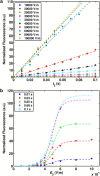
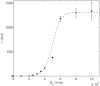
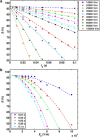
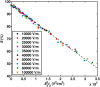
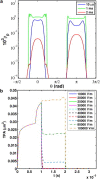
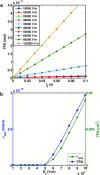
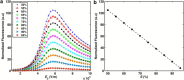
The efficacy of electroporation is known to vary significantly across a wide variety of biological research and clinical applications, but as of this writing, a generalized approach to simultaneously improve efficiency and maintain viability has not been available in the literature. To address that discrepancy, we here outline an approach that is based on the mapping of the scaling relationships among electroporation-mediated molecular delivery, cellular viability, and electric pulse parameters. The delivery of Fluorescein-Dextran into 3T3 mouse fibroblast cells was used as a model system. The pulse was rationally split into two sequential phases: a first precursor for permeabilization, followed by a second one for molecular delivery. Extensive data in the parameter space of the second pulse strength and duration were collected and analyzed with flow cytometry. The fluorescence intensity correlated linearly with the second pulse duration, confirming the dominant role of electrophoresis in delivery. The delivery efficiency exhibited a characteristic sigmoidal dependence on the field strength. An examination of short-term cell death using 7-Aminoactinomycin D demonstrated a convincing linear correlation with respect to the electrical energy. Based on these scaling relationships, an optimal field strength becomes identifiable. A model study was also performed, and the results were compared with the experimental data to elucidate underlying mechanisms. The comparison reveals the existence of a critical transmembrane potential above which delivery with the second pulse becomes effective. Together, these efforts establish a general route to enhance the functionality of electroporation.
Copyright © 2014 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- André F., Mir L.M. DNA electrotransfer: its principles and an updated review of its therapeutic applications. Gene Ther. 2004;11(Suppl 1):S33–S42. - PubMed
-
- Gehl J., Skovsgaard T., Mir L.M. Enhancement of cytotoxicity by electropermeabilization: an improved method for screening drugs. Anticancer Drugs. 1998;9:319–325. - PubMed
-
- Heller R., Shirley S., Heller L. Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE; New York: 2011. Electroporation based gene therapy—from the bench to the bedside; pp. 736–738. - PubMed
-
- Teissié J., Escoffre J.M., Golzio M. Drug delivery by electropulsation: recent developments in oncology. Int. J. Pharm. 2012;423:3–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

