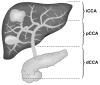
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 24560108
- PMCID: PMC4007210
- DOI: 10.1016/j.soc.2013.10.004
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
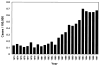
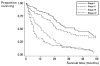
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) is a rare tumor, with an increasing incidence worldwide and an overall poor prognosis. Symptoms are usually nonspecific, contributing to an advanced tumor stage at diagnosis. The staging system for ICC has recently been updated and is based on number of lesions, vascular invasion, and lymph node involvement. Complete surgical resection to negative margins remains the only potentially curable treatment for ICC. Gemcitabine-based adjuvant therapy can be offered based on limited data from patients with unresectable ICC. Overall 5-year survivals after resection range from 17% to 44%, with median survivals of 19 to 43 months.
Keywords: Bile duct neoplasms; Cholangiocarcinoma; Intrahepatic bile duct cancer; Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; Peripheral cholangiocarcinoma.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Shaib Y, El-Serag HB. The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2004;24(2):115–25. - PubMed
-
- Patel T. Increasing incidence and mortality of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Hepatology. 2001;33(6):1353–7. - PubMed
-
- Everhart JE, Ruhl CE. Burden of digestive diseases in the United States Part III: liver, biliary tract, and pancreas. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(4):1134–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

