Implications of cellular models of dopamine neurons for schizophrenia
- PMID: 24560140
- PMCID: PMC4351765
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-397897-4.00011-5
Implications of cellular models of dopamine neurons for schizophrenia
Abstract
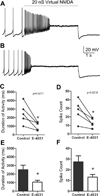
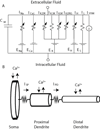
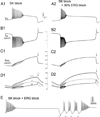
Midbrain dopamine neurons are pacemakers in vitro, but in vivo they fire less regularly and occasionally in bursts that can lead to a temporary cessation in firing produced by depolarization block. The therapeutic efficacy of antipsychotic drugs used to treat the positive symptoms of schizophrenia has been attributed to their ability to induce depolarization block within a subpopulation of dopamine neurons. We summarize the results of experiments characterizing the physiological mechanisms underlying the ability of these neurons to enter depolarization block in vitro, and our computational simulations of those experiments. We suggest that the inactivation of voltage-dependent Na(+) channels, and, in particular, the slower component of this inactivation, is critical in controlling entry into depolarization block. In addition, an ether-a-go-related gene (ERG) K(+) current also appears to be involved by delaying entry into and speeding recovery from depolarization block. Since many antipsychotic drugs share the ability to block this current, ERG channels may contribute to the therapeutic effects of these drugs.
Keywords: Antipsychotic drugs; Bursting; Depolarization block; Ether-a-go-go-related gene (ERG) potassium current; K(v)11; Pacemaker; Substantia nigra; Ventral tegmental area.
© 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures










References
-
- Bernheimer H, Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O, Jellinger K, Seitelberger F. Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntingdon: Clinical, morphological, and neurochemical correlations. J Neurosci. 1973;20:415–455. - PubMed
-
- Bloom FE, Roth RH, Cooper JR. The biochemical basis of neuropharmacology. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1991.
-
- Bunney BS, Grace AA. Acute and chronic haloperidol treatment: comparison of effects on nigral dopaminergic cell activity. Life Sci. 1978;23:1715–1727. - PubMed
-
- Canavier CC, Oprisan SA, Callaway J, Ji H, Shepard PD. Computational model predicts a role for ERG current in repolarizing plateau potentials in dopamine neurons: implications for modulation of neuronal activity. J. Neurophysiol. 2007;98:3006–3022. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson A, Lindqvist M. Effect of chlorpromazine or haloperidol on formation of 3-methoxytyramine and normetanephrine in mouse brain. Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. (Copenh) 1963;20:140–144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

