Astrocytes protect against diazinon- and diazoxon-induced inhibition of neurite outgrowth by regulating neuronal glutathione
- PMID: 24561003
- PMCID: PMC3999384
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tox.2014.01.010
Astrocytes protect against diazinon- and diazoxon-induced inhibition of neurite outgrowth by regulating neuronal glutathione
Abstract
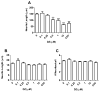
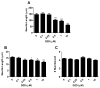
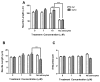
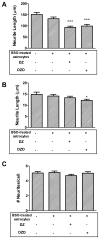
Evidence demonstrating that human exposure to various organophosphorus insecticides (OPs) is associated with neurobehavioral deficits in children continues to emerge. The present study focused on diazinon (DZ) and its active oxygen metabolite, diazoxon (DZO), and explored their ability to impair neurite outgrowth in rat primary hippocampal neurons as a mechanism of developmental neurotoxicity. Both DZ and DZO (0.5-10 μM) significantly inhibited neurite outgrowth in hippocampal neurons, at concentrations devoid of any cyototoxicity. These effects appeared to be mediated by oxidative stress, as they were prevented by antioxidants (melatonin, N-t-butyl-alpha-phenylnitrone, and glutathione ethyl ester). Inhibition of neurite outgrowth was observed at concentrations below those required to inhibit the catalytic activity of acetylcholinesterase. The presence of astrocytes in the culture was able to provide protection against inhibition of neurite outgrowth by DZ and DZO. Astrocytes increased neuronal glutathione (GSH) in neurons, to levels comparable to those of GSH ethyl ester. Astrocytes depleted of GSH by L-buthionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine no longer conferred protection against DZ- and DZO-induced inhibition of neurite outgrowth. The findings indicate that DZ and DZO inhibit neurite outgrowth in hippocampal neurons by mechanisms involving oxidative stress, and that these effects can be modulated by astrocytes and astrocyte-derived GSH. Oxidative stress from other chemical exposures, as well as genetic abnormalities that result in deficiencies in GSH synthesis and regulation, may render individuals more susceptible to these developmental neurotoxic effects of OPs.
Keywords: Diazinon; Diazoxon; Glial–neuronal interactions; Glutathione; Neurite outgrowth; Organophosphorus insecticide.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diazinon and diazoxon impair the ability of astrocytes to foster neurite outgrowth in primary hippocampal neurons.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Feb 1;274(3):372-82. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2013.11.023. Epub 2013 Dec 14. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24342266 Free PMC article.
-
Organophosphorus insecticides chlorpyrifos and diazinon and oxidative stress in neuronal cells in a genetic model of glutathione deficiency.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007 Mar;219(2-3):181-9. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.09.016. Epub 2006 Oct 4. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17084875
-
Diazinon oxon affects the differentiation of mouse N2a neuroblastoma cells.Arch Toxicol. 2009 Apr;83(4):373-80. doi: 10.1007/s00204-008-0339-1. Epub 2008 Jul 17. Arch Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 18633600
-
Effect of organophosphorus insecticides and their metabolites on astroglial cell proliferation.Toxicology. 2005 Nov 15;215(3):182-90. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2005.07.004. Epub 2005 Aug 15. Toxicology. 2005. PMID: 16102884
-
Glutathione Metabolism of the Brain-The Role of Astrocytes.J Neurochem. 2025 May;169(5):e70073. doi: 10.1111/jnc.70073. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 40313177 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Genetic Polymorphisms in Glutamate-Cysteine Ligase, a Key Enzyme of Glutathione Biosynthesis, on Ischemic Stroke Risk and Brain Infarct Size.Life (Basel). 2022 Apr 18;12(4):602. doi: 10.3390/life12040602. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455093 Free PMC article.
-
Role of biotransformation in the diazinon-induced toxicity in HepG2 cells and antioxidant protection by tetrahydrocurcumin.Toxicol Rep. 2022 Dec 12;10:32-39. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2022.12.005. eCollection 2023. Toxicol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36578673 Free PMC article.
-
The Precursor to Glutathione (GSH), γ-Glutamylcysteine (GGC), Can Ameliorate Oxidative Damage and Neuroinflammation Induced by Aβ40 Oligomers in Human Astrocytes.Front Aging Neurosci. 2019 Aug 8;11:177. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00177. eCollection 2019. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31440155 Free PMC article.
-
N-Acetyl-l-Cysteine Protects Astrocytes against Proteotoxicity without Recourse to Glutathione.Mol Pharmacol. 2017 Nov;92(5):564-575. doi: 10.1124/mol.117.109926. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Mol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28830914 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants and Neuron-Astrocyte Interplay in Brain Physiology: Melatonin, a Neighbor to Rely on.Neurochem Res. 2021 Jan;46(1):34-50. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-02972-w. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Neurochem Res. 2021. PMID: 31989469 Review.
References
-
- Anderson ME. Glutathione: an overview of biosynthesis and modulation. Chem Biol Interact. 1998:111–112. 1–14. - PubMed
-
- Axelrad JC, Howard CV, McLean WG. The effects of acute pesticide exposure on neuroblastoma cells chronically exposed to diazinon. Toxicology. 2003;185:67–78. - PubMed
-
- Ayoama K, Su SW, Hamby AM, liu J, Chan J, Chen Y, et al. Neuronal glutathione deficiency and age-dependent neurodegeneration in the EAAC1 deficient mouse. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:119–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

