Crystal structure of the RNA demethylase ALKBH5 from zebrafish
- PMID: 24561204
- PMCID: PMC3982313
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2014.02.021
Crystal structure of the RNA demethylase ALKBH5 from zebrafish
Abstract
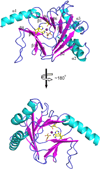
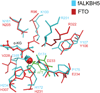
ALKBH5, a member of AlkB family proteins, has been reported as a mammalian N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) RNA demethylase. Here we report the crystal structure of zebrafish ALKBH5 (fALKBH5) with the resolution of 1.65Å. Structural superimposition shows that fALKBH5 is comprised of a conserved jelly-roll motif. However, it possesses a loop that interferes potential binding of a duplex nucleic acid substrate, suggesting an important role in substrate selection. In addition, several active site residues are different between the two known m(6)A RNA demethylases, ALKBH5 and FTO, which may result in their slightly different pathways of m(6)A demethylation.
Keywords: ALKBH5; Crystal structure; Demethylation; N(6)-Hydroxymethyladenosine.
Copyright © 2014 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Crystal structures of the human RNA demethylase Alkbh5 reveal basis for substrate recognition.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 25;289(17):11571-11583. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.546168. Epub 2014 Mar 10. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24616105 Free PMC article.
-
Structures of human ALKBH5 demethylase reveal a unique binding mode for specific single-stranded N6-methyladenosine RNA demethylation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jun 20;289(25):17299-311. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.550350. Epub 2014 Apr 28. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24778178 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of human RNA N⁶-methyladenine demethylase ALKBH5 provides insights into its mechanisms of nucleic acid recognition and demethylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Apr;42(7):4741-54. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku085. Epub 2014 Jan 30. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24489119 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic RNA modifications in disease.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2014 Jun;26:47-52. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2014.05.006. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2014. PMID: 25005745 Review.
-
FTO, m6 Am , and the hypothesis of reversible epitranscriptomic mRNA modifications.FEBS Lett. 2018 Jun;592(12):2012-2022. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13092. Epub 2018 May 24. FEBS Lett. 2018. PMID: 29754392 Review.
Cited by
-
ALKBH5 gene polymorphisms and Wilms tumor risk in Chinese children: A five-center case-control study.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Jun;34(6):e23251. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23251. Epub 2020 Feb 24. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 32091154 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of DNA and RNA Methylation on Radiobiology and Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 12;19(2):555. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020555. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29439529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Insights into N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Modification in the Transcriptome.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018 Apr;16(2):85-98. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2018.03.001. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29709557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-Adenosine Methylation (m6A) RNA Modification: an Emerging Role in Cardiovascular Diseases.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2021 Oct;14(5):857-872. doi: 10.1007/s12265-021-10108-w. Epub 2021 Feb 25. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33630241 Review.
-
Multi-substrate selectivity based on key loops and non-homologous domains: new insight into ALKBH family.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Jan;78(1):129-141. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03594-9. Epub 2020 Jul 8. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32642789 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bokar JA. The biosynthesis and functional roles of methylated nucleosides in eukaryotic mRNA. Fine-tuning of RNA functions by modification and editing, topics in current genetics. 2005 Springer;12:141–177.
-
- Beemon K, Keith J. Localization of N6-methyladenosine in the Rous sarcoma virus genome. J. Mol. Biol. 1977;113:165–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

