Phospholipid profiles of control and glaucomatous human aqueous humor
- PMID: 24561385
- PMCID: PMC3995849
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biochi.2014.01.020
Phospholipid profiles of control and glaucomatous human aqueous humor
Abstract
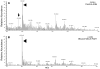
To compare phospholipid (phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylinositol) profiles of human control and glaucomatous aqueous humor (AQH). AQH samples were procured during surgery from human POAG and control subjects (n = 15 each). Samples were used following institutional review board approved protocols and adhering to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Lipid extraction was performed using a modification of the Bligh and Dyer method, protein concentrations were determined using the Bradford's method, and select samples were confirmed with Densitometry of PHAST gels. Lipids were identified and subjected to ratiometric quantification using a TSQ Quantum Access Max triple quadrupole mass spectrometer utilizing precursor ion scan (PIS) or neutral ion loss scan (NLS) using appropriate class specific lipid standards in a two step quantification process. The comparative profiles of phosphatidylcholines, phosphatidylserines, phosphatidylethanolamines and phosphatidylinositols between control and glaucomatous AQH showed several species common between them. A number of unique lipids in all four phospholipid classes were also identified in control eyes that were absent in glaucomatous eyes and vice versa. A number of phospholipids were found to be uniquely present in control, but absent in glaucomatous AQH and vice versa. Compared with a previous study of control and POAG red blood cells, a number of these phospholipids are absent locally (AQH).
Keywords: Aqueous humor; Glaucoma; Lipidomics; Mass spectrometry; Phospholipids.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative phospholipid profiles of control and glaucomatous human trabecular meshwork.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Apr 30;54(4):3037-44. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10517. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23557733 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol and glycosphingolipids of human trabecular meshwork and aqueous humor: comparative profiles from control and glaucomatous donors.Curr Eye Res. 2013 Oct;38(10):1017-26. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2013.803123. Epub 2013 Jun 21. Curr Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23790057
-
Sphingolipids and ceramides in human aqueous humor.Mol Vis. 2013 Sep 19;19:1966-84. eCollection 2013. Mol Vis. 2013. PMID: 24068864 Free PMC article.
-
Mass spectrometric analyses of phospholipids in the S334ter-3 rat model of retinal degeneration.Mol Vis. 2014 Nov 11;20:1605-11. eCollection 2014. Mol Vis. 2014. PMID: 25489232 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipid distributions and fatty acid composition of lysophosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylcholine in rabbit aqueous humor, lens and vitreous.Exp Eye Res. 1976 Jun;22(6):569-76. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(76)90001-4. Exp Eye Res. 1976. PMID: 776636 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Phospholipidomic Studies in Human Cornea From Climatic Droplet Keratopathy.J Cell Biochem. 2017 Nov;118(11):3920-3931. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26045. Epub 2017 May 23. J Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28401586 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Deimination in Regenerative Reprogramming of Neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Apr;56(4):2618-2639. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1262-y. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30051351 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Lipid Composition in Human Breast Milk and Their Correlation with Infant Neurodevelopment.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Nov 1;18(21):11501. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182111501. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34770016 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the Lipid Profile of Aqueous Humor From Diabetic Cataract Patients.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022 Nov 1;11(11):5. doi: 10.1167/tvst.11.11.5. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 36342707 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic analysis of aqueous humor reveals potential metabolite biomarkers for differential detection of macular edema.Eye Vis (Lond). 2023 Apr 1;10(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s40662-023-00331-8. Eye Vis (Lond). 2023. PMID: 37004107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weinreb RN, Khaw PT. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Lancet. 2004;363:1711–1720. - PubMed
-
- Asrani S, Zeimer R, Wilensky J, Gieser D, Vitale S, Lindenmuth K. Large diurnal fluctuations in intraocular pressure are an independent risk factor in patients with glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2000;9:134–142. - PubMed
-
- Morrison JC, Acott TS. Anatomy and physiology of aqueous humor outflow. In: Morrison JC, Pollack IP, editors. Glaucoma Science and Practice. Thieme Medical Publishers Inc; New York: 2003. pp. 34–41.
-
- Krupin T, Wax M, Moolchandani J. Aqueous production. Trans Ophthalmol Soc U K. 1986;105(Pt 2):156–161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

