Nucleus accumbens-specific interventions in RGS9-2 activity modulate responses to morphine
- PMID: 24561386
- PMCID: PMC4059906
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2014.45
Nucleus accumbens-specific interventions in RGS9-2 activity modulate responses to morphine
Abstract
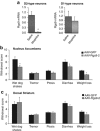
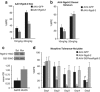
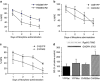
Regulator of G protein signalling 9-2 (Rgs9-2) modulates the actions of a wide range of CNS-acting drugs by controlling signal transduction of several GPCRs in the striatum. RGS9-2 acts via a complex mechanism that involves interactions with Gα subunits, the Gβ5 protein, and the adaptor protein R7BP. Our recent work identified Rgs9-2 complexes in the striatum associated with acute or chronic exposures to mu opioid receptor (MOR) agonists. In this study we use several new genetic tools that allow manipulations of Rgs9-2 activity in particular brain regions of adult mice in order to better understand the mechanism via which this protein modulates opiate addiction and analgesia. We used adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) to express forms of Rgs9-2 in the dorsal and ventral striatum (nucleus accumbens, NAc) in order to examine the influence of this protein in morphine actions. Consistent with earlier behavioural findings from constitutive Rgs9 knockout mice, we show that Rgs9-2 actions in the NAc modulate morphine reward and dependence. Notably, Rgs9-2 in the NAc affects the analgesic actions of morphine as well as the development of analgesic tolerance. Using optogenetics we demonstrate that activation of Channelrhodopsin2 in Rgs9-2-expressing neurons, or in D1 dopamine receptor (Drd1)-enriched medium spiny neurons, accelerates the development of morphine tolerance, whereas activation of D2 dopamine receptor (Drd2)-enriched neurons does not significantly affect the development of tolerance. Together, these data provide new information on the signal transduction mechanisms underlying opiate actions in the NAc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A unique role of RGS9-2 in the striatum as a positive or negative regulator of opiate analgesia.J Neurosci. 2011 Apr 13;31(15):5617-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4146-10.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21490202 Free PMC article.
-
Inputs from the basolateral amygdala to the nucleus accumbens shell control opiate reward magnitude via differential dopamine D1 or D2 receptor transmission.Eur J Neurosci. 2012 Jan;35(2):279-90. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07943.x. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Eur J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22236063
-
Regulator of G-Protein Signaling 7 Regulates Reward Behavior by Controlling Opioid Signaling in the Striatum.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Aug 1;80(3):235-45. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.07.026. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26364547 Free PMC article.
-
Reflections on: "A general role for adaptations in G-Proteins and the cyclic AMP system in mediating the chronic actions of morphine and cocaine on neuronal function".Brain Res. 2016 Aug 15;1645:71-4. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.12.039. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 26740398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
μ-Opioid receptors and regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) proteins: from a symposium on new concepts in mu-opioid pharmacology.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012 Mar 1;121(3):173-80. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.10.027. Epub 2011 Nov 29. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012. PMID: 22129844 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nociception and pain: lessons from optogenetics.Front Behav Neurosci. 2014 Mar 25;8:69. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2014.00069. eCollection 2014. Front Behav Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24723861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic mouse models in opioid research: current status and future directions.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2024 May;131(5):491-494. doi: 10.1007/s00702-024-02762-6. Epub 2024 Mar 4. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2024. PMID: 38436758 Review.
-
RGS9-2--controlled adaptations in the striatum determine the onset of action and efficacy of antidepressants in neuropathic pain states.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 8;112(36):E5088-97. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1504283112. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26305935 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of ubiquitin-proteasome system and regulator of G protein signaling 4 in behavioral sensitization induced by a single morphine exposure.Brain Behav. 2023 Mar;13(3):e2922. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2922. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 36793204 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of RGSz1 function optimizes the actions of opioid analgesics by mechanisms that involve the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Feb 27;115(9):E2085-E2094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707887115. Epub 2018 Feb 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 29440403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander GE, DeLong MR, Strick PL. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:357–381. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GR, Semenov A, Song JH, Martemyanov KA. The membrane anchor R7BP controls the proteolytic stability of the striatal specific RGS protein, RGS9-2. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:4772–4781. - PubMed
-
- Bailey CD, Connor M. Opioids: cellular mechanisms of tolerance and physical actions of Spinophilin Regulate mu opioid receptor function. Neuron 58: 238- dependence. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2005;5:60–68. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

