Role of the SIK2-p35-PJA2 complex in pancreatic β-cell functional compensation
- PMID: 24561619
- PMCID: PMC4107453
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2919
Role of the SIK2-p35-PJA2 complex in pancreatic β-cell functional compensation
Erratum in
- Nat Cell Biol. 2014 Apr;16(4):382
Abstract
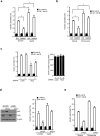
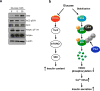
Energy sensing by the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is of fundamental importance in cell biology. In the pancreatic β-cell, AMPK is a central regulator of insulin secretion. The capacity of the β-cell to increase insulin output is a critical compensatory mechanism in prediabetes, yet its molecular underpinnings are unclear. Here we delineate a complex consisting of the AMPK-related kinase SIK2, the CDK5 activator CDK5R1 (also known as p35) and the E3 ligase PJA2 essential for β-cell functional compensation. Following glucose stimulation, SIK2 phosphorylates p35 at Ser 91, to trigger its ubiquitylation by PJA2 and promote insulin secretion. Furthermore, SIK2 accumulates in β-cells in models of metabolic syndrome to permit compensatory secretion; in contrast, β-cell knockout of SIK2 leads to accumulation of p35 and impaired secretion. This work demonstrates that the SIK2-p35-PJA2 complex is essential for glucose homeostasis and provides a link between p35-CDK5 and the AMPK family in excitable cells.
Figures
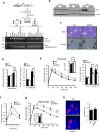
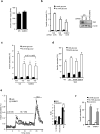

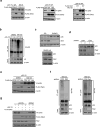
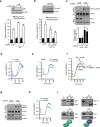

Comment in
-
SIK2 regulates insulin secretion.Nat Cell Biol. 2014 Mar;16(3):210-2. doi: 10.1038/ncb2925. Nat Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24576898
References
-
- Nolan CJ, Damm P, Prentki M. Type 2 diabetes across generations: from pathophysiology to prevention and management. Lancet. 2011;378:169–181. - PubMed
-
- Florez JC. Newly identified loci highlight beta cell dysfunction as a key cause of type 2 diabetes: where are the insulin resistance genes? Diabetologia. 2008;51:1100–1110. - PubMed
-
- Nolan CJ. Failure of islet beta-cell compensation for insulin resistance causes type 2 diabetes: what causes non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis? Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology. 2010;25:1594–1597. - PubMed
-
- Kahn SE. The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of Type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2003;46:3–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

