Dynamics of short- and long-term association between a bacterial plant pathogen and its arthropod vector
- PMID: 24561664
- PMCID: PMC3932477
- DOI: 10.1038/srep04155
Dynamics of short- and long-term association between a bacterial plant pathogen and its arthropod vector
Abstract
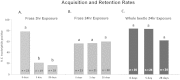
The dynamics of association between pathogens and vectors can strongly influence epidemiology. It has been proposed that wilt disease epidemics in cucurbit populations are sustained by persistent colonization of beetle vectors (Acalymma vittatum) by the bacterial phytopathogen Erwinia tracheiphila. We developed a qPCR method to quantify E. tracheiphila in whole beetles and frass and used it to assess pathogen acquisition and retention following variable exposure to infected plants. We found that (i) E. tracheiphila is present in frass in as little as three hours after feeding on infected plants and can be transmitted with no incubation period by vectors given brief exposure to infected plants, but also by persistently colonized vectors several weeks following exposure; (ii) duration of exposure influences rates of long-term colonization; (iii) frass infectivity (assessed via inoculation experiments) reflects bacterial levels in frass samples across time; and (iv) vectors rarely clear E. tracheiphila infections, but suffer no apparent loss of fitness. These results describe a pattern conducive to the effective maintenance of E. tracheiphila within cucurbit populations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Floral transmission of Erwinia tracheiphila by cucumber beetles in a wild Cucurbita pepo.Environ Entomol. 2010 Feb;39(1):140-8. doi: 10.1603/EN09190. Environ Entomol. 2010. PMID: 20146850
-
Disease interactions in a shared host plant: effects of pre-existing viral infection on cucurbit plant defense responses and resistance to bacterial wilt disease.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 14;8(10):e77393. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077393. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24155951 Free PMC article.
-
Insect frass as a pathway for transmission of bacterial wilt of cucurbits.Environ Entomol. 2009 Apr;38(2):395-403. doi: 10.1603/022.038.0212. Environ Entomol. 2009. PMID: 19389288
-
Understanding pathogen survival and transmission by arthropod vectors to prevent human disease.Science. 2022 Sep 30;377(6614):eabc2757. doi: 10.1126/science.abc2757. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Science. 2022. PMID: 36173836 Review.
-
Effects of pathogens on sensory-mediated interactions between plants and insect vectors.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2016 Aug;32:53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2016.06.012. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27362574 Review.
Cited by
-
Zucchini Yellow Mosaic Virus Infection Limits Establishment and Severity of Powdery Mildew in Wild Populations of Cucurbita pepo.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Jun 13;9:792. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00792. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29951077 Free PMC article.
-
A horizontally acquired expansin gene increases virulence of the emerging plant pathogen Erwinia tracheiphila.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 10;10(1):21743. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78157-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33303810 Free PMC article.
-
Beetles as Plant Pathogen Vectors.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 11;12:748093. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.748093. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34721475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flowering plant composition shapes pathogen infection intensity and reproduction in bumble bee colonies.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 May 26;117(21):11559-11565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2000074117. Epub 2020 May 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32393622 Free PMC article.
-
Aster leafhopper survival and reproduction, and Aster yellows transmission under static and fluctuating temperatures, using ddPCR for phytoplasma quantification.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 10;8(1):227. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18437-0. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29321551 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ng J. C. K. & Falk B. W. Virus-vector interactions mediating nonpersistent and semipersistent transmission of plant viruses. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 44, 183–212 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Purcell A. H. & Hopkins D. L. Fastidious xylem-limited bacterial plant pathogens. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 34, 131–151 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Salazar C., Gildow F. E., Fleischer S. J., Cox-Foster D. & Lukezic F. L. Alimentary canal of adult Acalymma vittata (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae): morphology and potential role in survival of Erwinia tracheiphila (Enterobacteriaceae). Can J of Ent 132, 1–13 (2000).
-
- Hogenhout S. A., Ammar E. D., Whitfield A. E. & Redinbaugh M. G. Insect vector interactions with persistently transmitted viruses. Annual Review Phytopathol 46, 327–359 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Madden L. V., Jeger M. J. & Van den Bosch F. A theoretical assessment of the effects of vector-virus transmission mechanism on plant virus disease epidemics. Phytopathology 90, 576–594 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

