Sparse, decorrelated odor coding in the mushroom body enhances learned odor discrimination
- PMID: 24561998
- PMCID: PMC4000970
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3660
Sparse, decorrelated odor coding in the mushroom body enhances learned odor discrimination
Abstract
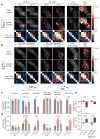
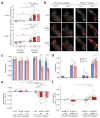
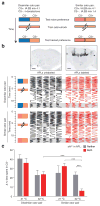
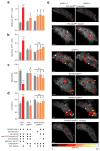
Sparse coding may be a general strategy of neural systems for augmenting memory capacity. In Drosophila melanogaster, sparse odor coding by the Kenyon cells of the mushroom body is thought to generate a large number of precisely addressable locations for the storage of odor-specific memories. However, it remains untested how sparse coding relates to behavioral performance. Here we demonstrate that sparseness is controlled by a negative feedback circuit between Kenyon cells and the GABAergic anterior paired lateral (APL) neuron. Systematic activation and blockade of each leg of this feedback circuit showed that Kenyon cells activated APL and APL inhibited Kenyon cells. Disrupting the Kenyon cell-APL feedback loop decreased the sparseness of Kenyon cell odor responses, increased inter-odor correlations and prevented flies from learning to discriminate similar, but not dissimilar, odors. These results suggest that feedback inhibition suppresses Kenyon cell activity to maintain sparse, decorrelated odor coding and thus the odor specificity of memories.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kanerva P. Sparse distributed memory. MIT Press; 1988.
-
- Albus JS. A theory of cerebellar function. Math Biosci. 1971;10:25–61.
-
- Treves A, Rolls ET. What determines the capacity of autoassociative memories in the brain? Network. 1991;2:371–397.
-
- Vinje WE, Gallant JL. Sparse coding and decorrelation in primary visual cortex during natural vision. Science. 2000;287:1273–1276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

