ALS2 mutations: juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and generalized dystonia
- PMID: 24562058
- PMCID: PMC3962990
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000254
ALS2 mutations: juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and generalized dystonia
Abstract
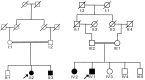
Objective: To determine the genetic etiology in 2 consanguineous families who presented a novel phenotype of autosomal recessive juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis associated with generalized dystonia.
Methods: A combination of homozygosity mapping and whole-exome sequencing in the first family and Sanger sequencing of candidate genes in the second family were used.
Results: Both families were found to have homozygous loss-of-function mutations in the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis 2 (juvenile) (ALS2) gene.
Conclusions: We report generalized dystonia and cerebellar signs in association with ALS2-related disease. We suggest that the ALS2 gene should be screened for mutations in patients who present with a similar phenotype.
Figures
References
-
- Yang Y, Hentati A, Deng HX, et al. The gene encoding alsin, a protein with three guanine-nucleotide exchange factor domains, is mutated in a form of recessive amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat Genet 2001;29:160–165 - PubMed
-
- Gros-Louis F, Meijer IA, Hand CK, et al. An ALS2 gene mutation causes hereditary spastic paraplegia in a Pakistani kindred. Ann Neurol 2003;53:144–145 - PubMed
-
- Shirakawa K, Suzuki H, Ito M, et al. Novel compound heterozygous ALS2 mutations cause juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in Japan. Neurology 2009;73:2124–2126 - PubMed
-
- Lesca G, Eymard-Pierre E, Santorelli FM, et al. Infantile ascending hereditary spastic paralysis (IAHSP): clinical features in 11 families. Neurology 2003;60:674–682 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical