Pathogens and host immunity in the ancient human oral cavity
- PMID: 24562188
- PMCID: PMC3969750
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.2906
Pathogens and host immunity in the ancient human oral cavity
Abstract
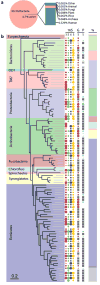
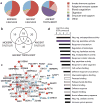
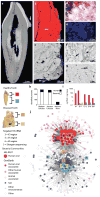
Calcified dental plaque (dental calculus) preserves for millennia and entraps biomolecules from all domains of life and viruses. We report the first, to our knowledge, high-resolution taxonomic and protein functional characterization of the ancient oral microbiome and demonstrate that the oral cavity has long served as a reservoir for bacteria implicated in both local and systemic disease. We characterize (i) the ancient oral microbiome in a diseased state, (ii) 40 opportunistic pathogens, (iii) ancient human-associated putative antibiotic resistance genes, (iv) a genome reconstruction of the periodontal pathogen Tannerella forsythia, (v) 239 bacterial and 43 human proteins, allowing confirmation of a long-term association between host immune factors, 'red complex' pathogens and periodontal disease, and (vi) DNA sequences matching dietary sources. Directly datable and nearly ubiquitous, dental calculus permits the simultaneous investigation of pathogen activity, host immunity and diet, thereby extending direct investigation of common diseases into the human evolutionary past.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Comment in
-
Ancient human oral plaque preserves a wealth of biological data.Nat Genet. 2014 Apr;46(4):321-3. doi: 10.1038/ng.2930. Nat Genet. 2014. PMID: 24675519
-
Calculus is a long-term reservoir of disease.Br Dent J. 2014 Apr;216(8):438. doi: 10.1038/sj.bdj.2014.307. Br Dent J. 2014. PMID: 24762878 No abstract available.
References
-
- Marsh PD. Are dental diseases examples of ecological catastrophes? Microbiology. 2003;149:279–294. - PubMed
-
- Pihlstrom BL, Michalowicz BS, Johnson NW. Periodontal diseases. Lancet. 2005;366:1809–1820. - PubMed
-
- Hujoel P. Dietary carbohydrates and dental-systemic diseases. J Dent Res. 2009;88:490–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- SRA/SRP029257
- SRA/SRS473742
- SRA/SRS473743
- SRA/SRS473744
- SRA/SRS473745
- SRA/SRS473746
- SRA/SRS473747
- SRA/SRS473748
- SRA/SRS473749
- SRA/SRS473750
- SRA/SRS473751
- SRA/SRS473752
- SRA/SRS473753
- SRA/SRS473754
- SRA/SRS473755
- SRA/SRS473756
- SRA/SRS473757
- SRA/SRS473758
- SRA/SRS473759
- SRA/SRS473760
- SRA/SRS473761
- SRA/SRS473762
- SRA/SRS473763
- SRA/SRS473764
- SRA/SRS473765
- SRA/SRS473766
- SRA/SRS473767
- SRA/SRS473768
- SRA/SRS473769
- SRA/SRS473770
- SRA/SRS473771
- SRA/SRS480529
- SRA/SRS480530
- SRA/SRS480531
- SRA/SRS480532
- SRA/SRS480533
- SRA/SRS480534
- SRA/SRS480535
- SRA/SRS480536
- SRA/SRS480537
- SRA/SRS480538
- SRA/SRS480539
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

