A systematic approach to design and prepare solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drug
- PMID: 24563175
- PMCID: PMC4037479
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-014-0093-z
A systematic approach to design and prepare solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drug
Abstract
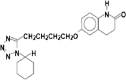
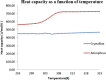
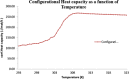
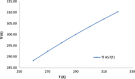
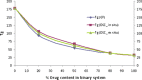
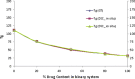
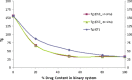
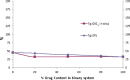
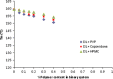
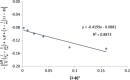
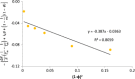
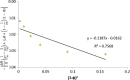
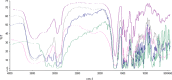
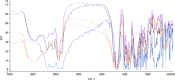
The objective of the present study was to define a systematic approach to design and prepare solid dispersions of poorly water-soluble drug. The systematic approach can be defined in four phases. In the first phase, glass forming ability is assessed, and in the second phase, probable excipients are screened. The screened excipients are evaluated (third phase) for glass transition temperatures (Tg) and miscibility studies according to Florey-Huggins interaction parameter. The predicted excipients are used to prepare the solid dispersion and evaluated for Tg and any interactions using Fourier transfer infrared studies (fourth phase), and the findings are correlated with phase three predictions. For this investigation, cilostazol (CIL) was selected as model drug, which was classified as a poor glass former. As per the physical chemical properties of CIL, ten excipients, both polymeric and non-polymeric, were selected and screened. Out of these, povidone, copovidone, hypromellose and Eudragit EPO were found theoretically miscible with CIL. After going through phase 2 to phase 4, only povidone, copovidone and hypromellose were confirmed as polymer of choice for preparing the solid dispersion of CIL with a prediction of better physical solid-state stability on the basis of good miscibility between drug and carrier.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Wetting Kinetics: an Alternative Approach Towards Understanding the Enhanced Dissolution Rate for Amorphous Solid Dispersion of a Poorly Soluble Drug.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015 Oct;16(5):1079-90. doi: 10.1208/s12249-014-0281-x. Epub 2015 Feb 12. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015. PMID: 25672820 Free PMC article.
-
Improved dissolution of a poorly water soluble drug in solid dispersions with polymeric and non-polymeric hydrophilic additives.Acta Pharm. 2008 Sep;58(3):257-74. doi: 10.2478/v10007-008-0016-1. Acta Pharm. 2008. PMID: 19103563
-
Physicochemical properties of tadalafil solid dispersions - Impact of polymer on the apparent solubility and dissolution rate of tadalafil.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015 Aug;94:106-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2015.04.031. Epub 2015 May 19. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015. PMID: 25998701
-
Miscibility, phase behavior, and mechanical properties of copovidone/HPMC ASLF and copovidone/Eudragit EPO polymer blends for hot-melt extrusion and 3D printing applications.Int J Pharm. 2025 Feb 10;670:125124. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2024.125124. Epub 2024 Dec 25. Int J Pharm. 2025. PMID: 40758126
-
A New Extrudable Form of Hypromellose: AFFINISOL™ HPMC HME.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016 Feb;17(1):106-19. doi: 10.1208/s12249-015-0395-9. Epub 2015 Sep 4. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2016. PMID: 26335416 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Wetting Kinetics: an Alternative Approach Towards Understanding the Enhanced Dissolution Rate for Amorphous Solid Dispersion of a Poorly Soluble Drug.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015 Oct;16(5):1079-90. doi: 10.1208/s12249-014-0281-x. Epub 2015 Feb 12. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015. PMID: 25672820 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilisation and Growth of Metastable Form II of Fluconazole in Amorphous Solid Dispersions.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Dec 20;12(1):12. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12010012. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31877666 Free PMC article.
-
Hot-Melt Extrusion: a Roadmap for Product Development.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021 Jun 17;22(5):184. doi: 10.1208/s12249-021-02017-7. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2021. PMID: 34142250 Review.
-
Disintegration mediated controlled release supersaturating solid dispersion formulation of an insoluble drug: design, development, optimization, and in vitro evaluation.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015 Feb;16(1):85-97. doi: 10.1208/s12249-014-0187-7. Epub 2014 Sep 5. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2015. PMID: 25190361 Free PMC article.
-
Physical Stability of Amorphous Solid Dispersions: a Physicochemical Perspective with Thermodynamic, Kinetic and Environmental Aspects.Pharm Res. 2018 Apr 23;35(6):125. doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2408-3. Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 29687226 Review.
References
-
- Van deWaterbeemd H, Lennernas H, Artursson P. Drug bioavailability: estimation of solubility, permeability, absorption and bioavailability. New York: Wiley-VCH; 2003.
-
- Habib MJ. Pharmaceutical solid dispersion technology. New York: CRC; 2000.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

