ABD1 is an Arabidopsis DCAF substrate receptor for CUL4-DDB1-based E3 ligases that acts as a negative regulator of abscisic acid signaling
- PMID: 24563203
- PMCID: PMC3967034
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.113.119974
ABD1 is an Arabidopsis DCAF substrate receptor for CUL4-DDB1-based E3 ligases that acts as a negative regulator of abscisic acid signaling
Abstract
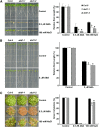
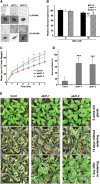
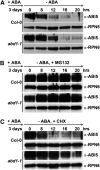
Members of the DDB1-CUL4-associated factors (DCAFs) family directly bind to DAMAGED DNA BINDING PROTEIN1 (DDB1) and function as the substrate receptors in CULLIN4-based E3 (CUL4) ubiquitin ligases, which regulate the selective ubiquitination of proteins. Here, we describe a DCAF protein, ABD1 (for ABA-hypersensitive DCAF1), that negatively regulates abscisic acid (ABA) signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. ABD1 interacts with DDB1 in vitro and in vivo, indicating that it likely functions as a CUL4 E3 ligase substrate receptor. ABD1 expression is induced by ABA, and mutations in ABD1 result in ABA- and NaCl-hypersensitive phenotypes. Loss of ABD1 leads to hyperinduction of ABA-responsive genes and higher accumulation of the ABA-responsive transcription factor ABA INSENSITIVE5 (ABI5), hypersensitivity to ABA during seed germination and seedling growth, enhanced stomatal closure, reduced water loss, and, ultimately, increased drought tolerance. ABD1 directly interacts with ABI5 in yeast two-hybrid assays and associates with ABI5 in vivo by coimmunoprecipitation, and the interaction was found in the nucleus by bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Furthermore, loss of ABD1 results in a retardation of ABI5 degradation by the 26S proteasome. Taken together, these data suggest that the DCAF-CUL4 E3 ubiquitin ligase assembled with ABD1 is a negative regulator of ABA responses by directly binding to and affecting the stability of ABI5 in the nucleus.
Figures






References
-
- Agarwal P.K., Agarwal P., Reddy M.K., Sopory S.K. (2006). Role of DREB transcription factors in abiotic and biotic stress tolerance in plants. Plant Cell Rep. 25: 1263–1274. - PubMed
-
- Angers S., Li T., Yi X., MacCoss M.J., Moon R.T., Zheng N. (2006). Molecular architecture and assembly of the DDB1-CUL4A ubiquitin ligase machinery. Nature 443: 590–593. - PubMed
-
- Aubert Y., Vile D., Pervent M., Aldon D., Ranty B., Simonneau T., Vavasseur A., Galaud J.P. (2010). RD20, a stress-inducible caleosin, participates in stomatal control, transpiration and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 51: 1975–1987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

