Cross-talk between two essential nutrient-sensitive enzymes: O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
- PMID: 24563466
- PMCID: PMC4036179
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.523068
Cross-talk between two essential nutrient-sensitive enzymes: O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)
Abstract
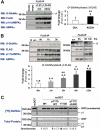
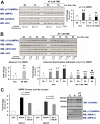
Nutrient-sensitive pathways regulate both O-GlcNAc transferase (OGT) and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), cooperatively connecting metabolic homeostasis to regulation of numerous intracellular processes essential for life. Similar to phosphorylation, catalyzed by kinases such as AMPK, O-GlcNAcylation is a highly dynamic Ser/Thr-specific post-translational modification of nuclear, cytoplasmic, and mitochondrial proteins catalyzed exclusively by OGT. OGT and AMPK target a multitude of intracellular proteins, with the net effect to protect cells from the damaging effects of metabolic stress. Despite hundreds of studies demonstrating significant overlap in upstream and downstream signaling processes, no study has investigated if OGT and AMPK can directly regulate each other. We show acute activation of AMPK alters the substrate selectivity of OGT in several cell lines and nuclear localization of OGT in C2C12 skeletal muscle myotubes. Nuclear localization of OGT affects O-GlcNAcylation of numerous nuclear proteins and acetylation of Lys-9 on histone 3 in myotubes. AMPK phosphorylates Thr-444 on OGT in vitro; phosphorylation of Thr-444 is tightly associated with AMPK activity and nuclear localization of OGT in myotubes, and phospho-mimetic T444E-OGT exhibits altered substrate selectivity. Conversely, the α- and γ-subunits of AMPK are O-GlcNAcylated, O-GlcNAcylation of the γ1-subunit increases with AMPK activity, and acute inhibition of O-GlcNAc cycling disrupts activation of AMPK. We have demonstrated significant cross-talk between the O-GlcNAc and AMPK systems, suggesting OGT and AMPK may cooperatively regulate nutrient-sensitive intracellular processes that mediate cellular metabolism, growth, proliferation, and/or tissue function.
Keywords: AMP-activated Kinase (AMPK); Histones; Nuclear Translocation; Nutrient Sensing; O-GlcNAc; O-GlcNAc Transferase; O-GlcNAcylation; Skeletal Muscle.
Figures
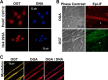

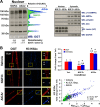


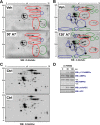
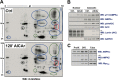


References
-
- Hanover J. A., Krause M. W., Love D. C. (2012) Post-translational modifications: Bittersweet memories: linking metabolism to epigenetics through O-GlcNAcylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 312–321 - PubMed
-
- Chatham J. C., Nöt L. G., Fülöp N., Marchase R. B. (2008) Hexosamine biosynthesis and protein O-glycosylation: the first line of defense against stress, ischemia, and trauma. Shock 29, 431–440 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01CA42486/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM037537/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA042486/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HV-00240/HV/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL107153/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK084949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK061671/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01HL107153/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24DK084949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM037537/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK61671/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

