True grit: programmed necrosis in antiviral host defense, inflammation, and immunogenicity
- PMID: 24563506
- PMCID: PMC3934821
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302426
True grit: programmed necrosis in antiviral host defense, inflammation, and immunogenicity
Abstract
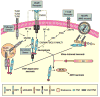
Programmed necrosis mediated by receptor interacting protein kinase (RIP)3 (also called RIPK3) has emerged as an alternate death pathway triggered by TNF family death receptors, pathogen sensors, IFNRs, Ag-specific TCR activation, and genotoxic stress. Necrosis leads to cell leakage and acts as a "trap door," eliminating cells that cannot die by apoptosis because of the elaboration of pathogen-encoded caspase inhibitors. Necrotic signaling requires RIP3 binding to one of three partners-RIP1, DAI, or TRIF-via a common RIP homotypic interaction motif. Once activated, RIP3 kinase targets the pseudokinase mixed lineage kinase domain-like to drive cell lysis. Although necrotic and apoptotic death can enhance T cell cross-priming during infection, mice that lack these extrinsic programmed cell death pathways are able to produce Ag-specific T cells and control viral infection. The entwined relationship of apoptosis and necrosis evolved in response to pathogen-encoded suppressors to support host defense and contribute to inflammation.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

