RNase E forms a complex with polynucleotide phosphorylase in cyanobacteria via a cyanobacterial-specific nonapeptide in the noncatalytic region
- PMID: 24563514
- PMCID: PMC3964918
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.043513.113
RNase E forms a complex with polynucleotide phosphorylase in cyanobacteria via a cyanobacterial-specific nonapeptide in the noncatalytic region
Abstract
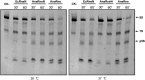
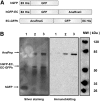
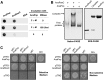
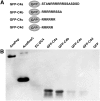
RNase E, a central component involved in bacterial RNA metabolism, usually has a highly conserved N-terminal catalytic domain but an extremely divergent C-terminal domain. While the C-terminal domain of RNase E in Escherichia coli recruits other components to form an RNA degradation complex, it is unknown if a similar function can be found for RNase E in other organisms due to the divergent feature of this domain. Here, we provide evidence showing that RNase E forms a complex with another essential ribonuclease-the polynucleotide phosphorylase (PNPase)-in cyanobacteria, a group of ecologically important and phylogenetically ancient organisms. Sequence alignment for all cyanobacterial RNase E proteins revealed several conserved and variable subregions in their noncatalytic domains. One such subregion, an extremely conserved nonapeptide (RRRRRRSSA) located near the very end of RNase E, serves as the PNPase recognition site in both the filamentous cyanobacterium Anabaena PCC7120 and the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC6803. These results indicate that RNase E and PNPase form a ribonuclease complex via a common mechanism in cyanobacteria. The PNPase-recognition motif in cyanobacterial RNase E is distinct from those previously identified in Proteobacteria, implying a mechanism of coevolution for PNPase and RNase E in different organisms.
Keywords: PNPase recognition site; RNA degradosome; RNase E; cyanobacteria.
Figures


References
-
- Arraiano CM, Andrade JM, Domingues S, Guinote IB, Malecki M, Matos RG, Moreira RN, Pobre V, Reis FP, Saramago M, et al. 2010. The critical role of RNA processing and degradation in the control of gene expression. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34: 883–923 - PubMed
-
- Blum E, Carpousis AJ, Higgins CF 1999. Polyadenylation promotes degradation of 3′-structured RNA by the Escherichia coli mRNA degradosome in vitro. J Biol Chem 274: 4009–4016 - PubMed
-
- Callaghan AJ, Aurikko JP, Ilag LL, Günter Grossmann J, Chandran V, Kühnel K, Poljak L, Carpousis AJ, Robinson CV, Symmons MF, et al. 2004. Studies of the RNA degradosome-organizing domain of the Escherichia coli ribonuclease RNase E. J Mol Biol 340: 965–979 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
