Empathy for social exclusion involves the sensory-discriminative component of pain: a within-subject fMRI study
- PMID: 24563529
- PMCID: PMC4321615
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsu038
Empathy for social exclusion involves the sensory-discriminative component of pain: a within-subject fMRI study
Abstract
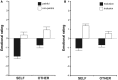
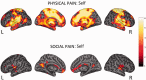
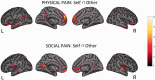
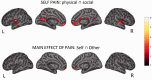
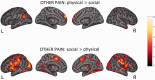
Recent research has shown that experiencing events that represent a significant threat to social bonds activates a network of brain areas associated with the sensory-discriminative aspects of pain. In the present study, we investigated whether the same brain areas are involved when witnessing social exclusion threats experienced by others. Using a within-subject design, we show that an ecologically valid experience of social exclusion recruits areas coding the somatosensory components of physical pain (posterior insular cortex and secondary somatosensory cortex). Furthermore, we show that this pattern of activation not only holds for directly experienced social pain, but also during empathy for social pain. Finally, we report that subgenual cingulate cortex is the only brain area conjointly active during empathy for physical and social pain. This supports recent theories that affective processing and homeostatic regulation are at the core of empathic responses.
Keywords: empathy; fMRI; physical pain; social exclusion; somatosensory cortex.
© The Author (2014). Published by Oxford University Press. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reduced empathic responses for sexually objectified women: An fMRI investigation.Cortex. 2018 Feb;99:258-272. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2017.11.020. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Cortex. 2018. PMID: 29294431
-
Meta-analytic evidence for common and distinct neural networks associated with directly experienced pain and empathy for pain.Neuroimage. 2011 Feb 1;54(3):2492-502. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.10.014. Epub 2010 Oct 12. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 20946964 Review.
-
Empathy for the social suffering of friends and strangers recruits distinct patterns of brain activation.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2013 Apr;8(4):446-54. doi: 10.1093/scan/nss019. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 22355182 Free PMC article.
-
Dispositional empathy predicts primary somatosensory cortex activity while receiving touch by a hand.Sci Rep. 2021 May 28;11(1):11294. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90344-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34050215 Free PMC article.
-
Shared and distinct functional networks for empathy and pain processing: a systematic review and meta-analysis of fMRI studies.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2020 Sep 24;15(7):709-723. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsaa090. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32608498 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Social exclusion reliably engages the default network: A meta-analysis of Cyberball.Neuroimage. 2021 Feb 15;227:117666. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117666. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 33359341 Free PMC article.
-
Placebo Analgesia Does Not Reduce Empathy for Naturalistic Depictions of Others' Pain in a Somatosensory Specific Way.Cereb Cortex Commun. 2021 Jun 2;2(3):tgab039. doi: 10.1093/texcom/tgab039. eCollection 2021. Cereb Cortex Commun. 2021. PMID: 34296184 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Emotional Conflicts and Pain Experience in Patients with Non-Specific Chronic Neck Pain: A Qualitative Study.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 4;14(13):4748. doi: 10.3390/jcm14134748. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40649122 Free PMC article.
-
Bodily sensations in social scenarios: Where in the body?PLoS One. 2019 Jun 11;14(6):e0206270. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206270. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31185013 Free PMC article.
-
Do Hostile School Environments Promote Social Deviance by Shaping Neural Responses to Social Exclusion?J Res Adolesc. 2018 Mar;28(1):103-120. doi: 10.1111/jora.12340. J Res Adolesc. 2018. PMID: 29460355 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amodio D, Frith C. Meeting of minds: the medial frontal cortex and social cognition. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2006;7(4):268–77. - PubMed
-
- Avenanti A, Bueti D, Galati G, Aglioti SM. Transcranial magnetic stimulation highlights the sensorimotor side of empathy for pain. Nature Neuroscience. 2005;8(7):955–60. - PubMed
-
- Beeney JE, Franklin RG, Jr, Levy KN, Adams RB., Jr I feel your pain: emotional closeness modulates neural responses to empathically experienced rejection. Social Neuroscience. 2011;6(4):369–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

