Crotalus durissus collilineatus Venom Induces TNF- α and IL-10 Production in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
- PMID: 24563803
- PMCID: PMC3915804
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/563628
Crotalus durissus collilineatus Venom Induces TNF- α and IL-10 Production in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
Abstract
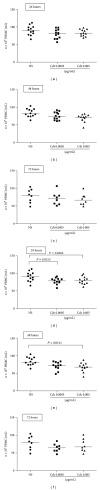
Snake venom has been the subject of numerous studies in an attempt to find properties and biological effects that may be beneficial to man. In this study we evaluated in vitro the effects of Crotalus durissus terrificus (Cdt) and Crotalus durissus collilineatus (Cdc) venom in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). At 24 h, a significant decrease of viable cells was observed in cells stimulated with the Cdc venom at 0.0005 mg/mL and 0.005 mg/mL compared to the negative control. At 48 h, a significant decrease of viable cells was observed only in cells stimulated with Cdc venom at 0.005 mg/mL. A significant increase of TNF- α and IL-10 was detected 48 hours after culture of PBMC with Cdc, but not with Cdt venom. The expression of CD69 and PD1 (programmed death-1), activation and regulatory cell markers, on CD8+ and CD8- T cells did not change in the presence of Cdt and Cdc venom. Our results suggest the presence of proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory components in the Cdc venom. Further analysis should be done to identify those Cdc venom components as it has been done for the Cdt venom by other authors, indicating that modulatory components are found in the venom of different species of Crotalus snakes.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Local and systemic effects caused by Crotalus durissus terrificus, Crotalus durissus collilineatus, and Crotalus durissus cascavella snake venoms in swiss mice.Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2019 Sep 5;52:e20180526. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0526-2018. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2019. PMID: 31508780
-
Snake venomics and antivenomics of Crotalus durissus subspecies from Brazil: assessment of geographic variation and its implication on snakebite management.J Proteomics. 2010 Aug 5;73(9):1758-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Jun 11. J Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20542151
-
Cross-neutralization of the neurotoxicity of Crotalus durissus terrificus and Bothrops jararacussu venoms by antisera against crotoxin and phospholipase A2 from Crotalus durissus cascavella venom.Toxicon. 2005 Nov;46(6):604-11. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2005.06.018. Epub 2005 Sep 12. Toxicon. 2005. PMID: 16157360
-
Geographic variation of individual venom profile of Crotalus durissus snakes.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2020 Aug 26;26:e20200016. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2020-0016. eCollection 2020. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32922444 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of antinociceptive fraction of snake venom from Crotalus durissus collilineatus crotamine-negative and its acute toxicity evaluation.Toxicon. 2016 Nov;122:145-151. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.10.008. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Toxicon. 2016. PMID: 27720975
Cited by
-
Bothrops bilineatus: An Arboreal Pitviper in the Amazon and Atlantic Forest.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 15;12:778302. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.778302. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34975866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Protein Composition and Bioactivity of Neoponera villosa Venom (Hymenoptera: Formicidae).Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Apr 21;17(4):513. doi: 10.3390/ijms17040513. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27110765 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of systemic inflammatory response and lung injury induced by Crotalus durissus cascavella venom.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 21;15(2):e0224584. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224584. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32084665 Free PMC article.
-
Acute toxicity, antinociceptive, and anti-inflammatory activities of the orally administered crotamine in mice.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2021 Aug;394(8):1703-1711. doi: 10.1007/s00210-021-02103-4. Epub 2021 May 20. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34014349
-
Fraction of C. d. collilineatus venom containing crotapotin protects PC12 cells against MPP + toxicity by activating the NGF-signaling pathway.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2024 Jun 14;30:e20230056. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2023-0056. eCollection 2024. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38915449 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Uetz P, Hallerman J. The TIGR Reptile Database. 2009, http://www.reptile-database.org.
-
- Sociedade Brasileira de Herpetologia—SBH. Lista Brasileira de Anfíbios e Répteis. Disponível em. 2011, http://www.sbherpetologia.org.br/
-
- Rosenfeld G. Acidentes por animais peçonhentos. In: Veronesi R, editor. Doenças Infecciosas e Parasitárias. 8th edition. Rio de Janeiro, Guanabara Koogan; 1991. pp. 951–962.
-
- Francischetti IMB, Gombarovits MEC, Valenzuela JG, Carlini CR, Guimarães JA. Intraspecific variation in the venoms of the South American rattlesnake (Crotalus durissus terrificus) Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C. 2000;127(1):23–36. - PubMed
-
- Cardoso JLC, França FOS, Wen F, Málaque S, Junior HV. Animais Peçonhentos no Brasil, Biologia, Clínica e Terapêutica dos Acidentes. 2th edition. São Paulo, Brazil: Sarvier; 2009.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

