The Impact of Hypotensive Epidural Anesthesia on Distal and Proximal Tissue Perfusion in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty
- PMID: 24563810
- PMCID: PMC3931466
- DOI: 10.4172/2155-6148.1000366
The Impact of Hypotensive Epidural Anesthesia on Distal and Proximal Tissue Perfusion in Patients Undergoing Total Hip Arthroplasty
Abstract
Little data exists to detail the effect of hypotensive epidural anesthesia on differential tissue oxygenation changes above and below the level of neuraxial blockade. This study was designed to investigate tissue oxygenation in a clinical setting, using non-invasive near-infrared spectroscopy.
Methods: Patients aged 18 to 85 years scheduled to undergo primary total hip arthroplasty were enrolled. Muscle oxygenation saturation was measured above and below the level of neuraxial blockade (deltoid and vastus lateralis muscles). Other continuously recorded parameters included cardiac output, stroke volume, heart rate, invasive mean arterial blood pressure and arterial oxygen saturation. Recordings of muscle oxygenation were compared over time separately for upper and lower extremity.
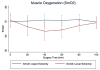
Results: 10 patients were enrolled. We found an intermittent and significant unadjusted decline of mean muscle oxygenation saturation in the vastus lateralis muscle during first part of the surgery (nadir 2nd quintile: 71.0% vs. 63.3%, p<0.0001). This decline was followed by a return to baseline towards the end of the surgery (71.0% vs. 69.1%, p=0.3429). Mean muscle oxygenation saturation did not change for the same period of time in the deltoid muscle. When adjusting for covariates, the changes in muscle tissue oxygenation remained significant.
Conclusion: These results indicate that muscle oxygenation saturation, a surrogate parameter for tissue perfusion, is decreased by hypotensive epidural anesthesia, but only within the functional limits of the neuraxial blockade. The etiology of these findings remains to be elucidated.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in tissue oxygenation following caudal epidural blockade in infants and children.Paediatr Anaesth. 2012 Nov;22(11):1068-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9592.2012.03925.x. Paediatr Anaesth. 2012. PMID: 22882639
-
The incidence of venous thromboembolism after total hip arthroplasty: a specific hypotensive epidural anesthesia protocol.J Arthroplasty. 1999 Jun;14(4):456-63. doi: 10.1016/s0883-5403(99)90101-8. J Arthroplasty. 1999. PMID: 10428226
-
Respiratory muscle unloading improves leg muscle oxygenation during exercise in patients with COPD.Thorax. 2008 Oct;63(10):910-5. doi: 10.1136/thx.2007.090167. Epub 2008 May 20. Thorax. 2008. PMID: 18492743
-
Hypotensive epidural anesthesia for total hip arthroplasty: a review.Acta Orthop Scand. 1996 Feb;67(1):91-107. doi: 10.3109/17453679608995620. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996. PMID: 8615115 Review.
-
The Use of Near Infrared Spectroscopy to Evaluate the Effect of Exercise on Peripheral Muscle Oxygenation in Patients with Lower Extremity Artery Disease: A Systematic Review.Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021 May;61(5):837-847. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2021.02.008. Epub 2021 Mar 30. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2021. PMID: 33810977
Cited by
-
Blood management in fast-track orthopedic surgery: an evidence-based narrative review.J Orthop Surg Res. 2019 Aug 20;14(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1296-5. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31429775 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effectiveness of Multi-Modal Blood Management in Bernese Periacetabular Osteotomy and Periacetabular Osteotomy with Proximal Femoral Osteotomy.Orthop Surg. 2020 Dec;12(6):1748-1752. doi: 10.1111/os.12794. Epub 2020 Oct 11. Orthop Surg. 2020. PMID: 33043623 Free PMC article.
-
Hypotensive Epidural Anesthesia Reduces Blood Loss in Pelvic and Sacral Bone Tumor Resections.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017 Mar;475(3):634-640. doi: 10.1007/s11999-016-4858-4. Epub 2016 May 12. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 27172818 Free PMC article.
-
Controlled hypotension during neuraxial anesthesia is not associated with increased odds of in-hospital common severe medical complications in patients undergoing elective primary total hip arthroplasty - A retrospective case control study.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 1;16(4):e0248419. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248419. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33793596 Free PMC article.
-
Perioperative blood management strategies for patients undergoing total knee replacement: Where do we stand now?World J Orthop. 2017 Jun 18;8(6):441-454. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i6.441. eCollection 2017 Jun 18. World J Orthop. 2017. PMID: 28660135 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. HCUPnet, Healthcare Cost and Utilization Project. USA:
-
- Kurtz S, Ong K, Lau E, Mowat F, Halpern M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:780–785. - PubMed
-
- Mauermann WJ, Shilling AM, Zuo Z. A comparison of neuraxial block versus general anesthesia for elective total hip replacement: a meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 2006;103:1018–1025. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources