Selective Neuronal and Brain Regional Expession of IL-2 in IL2P 8-GFP Transgenic Mice: Relation to Sensorimotor Gating
- PMID: 24563821
- PMCID: PMC3931468
- DOI: 10.4172/2161-0460.1000127
Selective Neuronal and Brain Regional Expession of IL-2 in IL2P 8-GFP Transgenic Mice: Relation to Sensorimotor Gating
Abstract
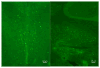
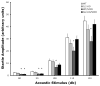
Brain-derived interleukin-2 (IL-2) has been implicated in diseases processes that arise during CNS development (e.g., autism) to neurodegenerative alterations involving neuroinflammation (e.g., Alzheimer's disease). Progress has been limited, however, because the vast majority of current knowledge of IL-2's actions on brain function and behavior is based on the use exogenously administered IL-2 to make inferences about the function of the endogenous cytokine. Thus, to identify the cell-type(s) and regional circuitry that express brain-derived IL-2, we used B6.Cg-Tg/ IL2-EGFP17Evr (IL2p8-GFP) transgenic mice, which express green fluorescent protein (GFP) in peripheral immune cells known to produce IL-2. We found that the IL2-GFP transgene was localized almost exclusively to NeuN-positive cells, indicating that the IL-2 is produced primarily by neurons. The IL2-GFP transgene was expressed in discrete nuclei throughout the rostral-caudal extent of the brain and brainstem, with the highest levels found in the cingulate, dorsal endopiriform nucleus, lateral septum, nucleus of the solitary tract, magnocellular/gigantocellular reticular formation, red nucleus, entorhinal cortex, mammilary bodies, cerebellar fastigial nucleus, and posterior interposed nucleus. Having identified IL-2 gene expression in brain regions associated with the regulation of sensorimotor gating (e.g., lateral septum, dorsal endopiriform nucleus, entorhinal cortex, striatum), we compared prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle response in congenic mice bred in our lab that have selective loss of the IL-2 gene in the brain versus the peripheral immune system, to test the hypothesis that brain-derived IL-2 plays a role in modulating PPI. We found that congenic mice devoid of IL-2 gene expression in both the brain and the peripheral immune system, exhibited a modest alteration of PPI. These finding suggest that IL2p8-GFP transgenic mice may be a useful tool to elucidate further the role of brain-derived IL-2 in normal CNS function and disease.
Keywords: Congenic mice; Interleukin-2; Prepulse inhibition; Sensorimotor gating.
Figures



References
-
- Petitto JM, Meola D, Huang Z. Interleukin-2 and the brain: dissecting central versus peripheral contributions using unique mouse models. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;934:301–311. - PubMed
-
- Sarder M, Abe K, Saito H, Nishiyama N. Comparative effect of IL-2 and IL-6 on morphology of cultured hippocampal neurons from fetal rat brain. Brain Res. 1996;715:9–16. - PubMed
-
- Sarder M, Saito H, Abe K. Interleukin-2 promotes survival and neurite extension of cultured neurons from fetal rat brain. Brain Res. 1993;625:347–350. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
