A novel in silico reverse-transcriptomics-based identification and blood-based validation of a panel of sub-type specific biomarkers in lung cancer
- PMID: 24564251
- PMCID: PMC3908344
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-14-S6-S5
A novel in silico reverse-transcriptomics-based identification and blood-based validation of a panel of sub-type specific biomarkers in lung cancer
Abstract
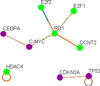
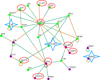
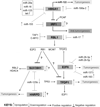
Lung cancer accounts for the highest number of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Early diagnosis significantly increases the disease-free survival rate and a large amount of effort has been expended in screening trials and the development of early molecular diagnostics. However, a gold standard diagnostic strategy is not yet available. Here, based on miRNA expression profile in lung cancer and using a novel in silico reverse-transcriptomics approach, followed by analysis of the interactome; we have identified potential transcription factor (TF) markers that would facilitate diagnosis of subtype specific lung cancer. A subset of seven TF markers has been used in a microarray screen and was then validated by blood-based qPCR using stage-II and IV non-small cell lung carcinomas (NSCLC). Our results suggest that overexpression of HMGA1, E2F6, IRF1, and TFDP1 and downregulation or no expression of SUV39H1, RBL1, and HNRPD in blood is suitable for diagnosis of lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma sub-types of NSCLC. Here, E2F6 was, for the first time, found to be upregulated in NSCLC blood samples. The miRNA-TF-miRNA interaction based molecular mechanisms of these seven markers in NSCLC revealed that HMGA1 and TFDP1 play vital roles in lung cancer tumorigenesis. The strategy developed in this work is applicable to any other cancer or disease and can assist in the identification of potential biomarkers.
Figures


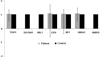
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA expression distinguishes SCLC from NSCLC lung tumor cells and suggests a possible pathological relationship between SCLCs and NSCLCs.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jun 17;29(1):75. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-29-75. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20624269 Free PMC article.
-
Five microRNAs in plasma as novel biomarkers for screening of early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.Respir Res. 2014 Nov 25;15(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12931-014-0149-3. Respir Res. 2014. PMID: 25421010 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of differentially expressed circulating serum microRNA for the diagnosis and prognosis of Indian non-small cell lung cancer patients.Curr Probl Cancer. 2020 Aug;44(4):100540. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2020.100540. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Curr Probl Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32007320 Review.
-
miR-1254 and miR-574-5p: serum-based microRNA biomarkers for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2011 Mar;6(3):482-8. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318208c785. J Thorac Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21258252
-
Molecular biomarkers of lung carcinoma.Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4(3):865-75. doi: 10.2741/E425. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012. PMID: 22201920 Review.
Cited by
-
Linking common non-coding RNAs of human lung cancer and M. tuberculosis.Bioinformation. 2018 Jun 30;14(6):337-345. doi: 10.6026/97320630014337. eCollection 2018. Bioinformation. 2018. PMID: 30237679 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of the E2F Transcription Factor Family in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Jul 2;15:5973-5984. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S369582. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35811776 Free PMC article.
-
BARHL1 Is Downregulated in Alzheimer's Disease and May Regulate Cognitive Functions through ESR1 and Multiple Pathways.Genes (Basel). 2017 Sep 28;8(10):245. doi: 10.3390/genes8100245. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28956815 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation profiles of bronchoscopic biopsies for the diagnosis of lung cancer.Clin Epigenetics. 2021 Feb 17;13(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01024-6. Clin Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 33596996 Free PMC article.
-
HMGA1 gene expression level in cancer tissue and blood samples of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients: preliminary report.Mol Genet Genomics. 2022 Nov;297(6):1505-1514. doi: 10.1007/s00438-022-01936-9. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Mol Genet Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35948739 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

