Agreement between Orbscan II, VuMAX UBM and Artemis-2 very-high frequency ultrasound scanner for measurement of anterior chamber depth
- PMID: 24564379
- PMCID: PMC3936803
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2415-14-20
Agreement between Orbscan II, VuMAX UBM and Artemis-2 very-high frequency ultrasound scanner for measurement of anterior chamber depth
Abstract
Background: The aim was to compare the anterior chamber depth (ACD) measurements taken with Orbscan II, ultrasound biomicroscopy (UBM) and the Artemis-2 VHF (very-high-frequency) ultrasound scanner in normal subjects.
Methods: In this prospective study, one eye from each of 60 normal subjects was randomly selected. Three subjects dropped out of the study because they were apprehensive about the UBM examination; their data were excluded entirely. Measurements of ACD were taken with the Orbscan II, UBM and Artemis-2 VHFUS. Results were obtained for coefficient of variance (CV) and intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC), and statistical analysis was by repeated-measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) for intra-observer repeatability. ANOVA and Bland-Altman analyses were used to determine limits of agreement (LOA) between the three instruments.
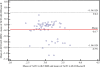
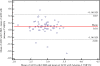
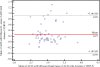
Results: The average ACD (± standard deviation) was 3.13 ± 0.34 mm, 2.96 ± 0.27 mm and 2.87 ± 0.31 mm for the Orbscan II, UBM and Artemis-2 VHFUS, respectively. The repeatability scores were 0.015 ± 0.014%, 0.08 ± 0.09% and 0.07 ± 0.06% for the Orbscan II, UBM and Artemis-2 VHFUS, respectively. The ICC for repeatability of Orbscan II, UBM and Artemis-2 VHFUS measurements was high and equal to 0.99%. The intra-observer repeatability scores of the ACD measurement p-values using Orbscan II, UBM and Artemis-2 VHFUS were 0.12, 0.70 and 0.10, respectively. The mean difference and standard deviations for ACD measurements using Orbscan II vs UBM, Orbscan II vs Artemis-2 VHFUS and UBM vs Artemis-2 VHFUS were 0.17 ± 0.31 mm, 0.27 ± 0.34 mm and 0.10 ± 0.18 mm, respectively. LOAs were 0.78 to -0.44 mm, 0.93 to -0.39 mm and 0.45 to -0.26 mm. ANOVA revealed a statistically significant difference between the Orbscan II, UBM and Artemis-2 VHFUS (p < 0.0001).
Conclusions: Measurements by the three instruments show high repeatability. UBM and the Artemis-2 VHFUS can be used interchangeably, but the Orbscan II cannot be used interchangeably with UBM or the Artemis-2 VHFUS.
Figures
References
-
- Devereux JG, Foster PJ, Baasanhu J, Uranchimeg D, Lee PS, Erdenbeleig T, Machin D, Johnson GJ, Alsbirk PH. Anterior chamber depth measurement as a screening tool for primary angle-closure glaucoma in an East Asian population. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000;118:257–263. doi: 10.1001/archopht.118.2.257. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Freedman KA, Brown SM, Mathews SM, Young RS. Pupil size and the ablation zone in laser refractive surgery: considerations based on geometric optics. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1924–1931;2003:29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

