Temporary threshold shift after impulse-noise during video game play: laboratory data
- PMID: 24564694
- PMCID: PMC4698154
- DOI: 10.3109/14992027.2013.865844
Temporary threshold shift after impulse-noise during video game play: laboratory data
Abstract
Objective: Prevention of temporary threshold shift (TTS) after laboratory-based exposure to pure-tones, broadband noise, and narrowband noise signals has been achieved, but prevention of TTS under these experimental conditions may not accurately reflect protection against hearing loss following impulse noise. This study used a controlled laboratory-based TTS paradigm that incorporated impulsive stimuli into the exposure protocol; development of this model could provide a novel platform for assessing proposed therapeutics.
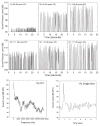
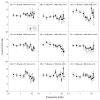
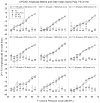
Design: Participants played a video game that delivered gunfire-like sound through headphones as part of a target practice game. Effects were measured using audiometric threshold evaluations and distortion product otoacoustic emissions (DPOAEs). The sound level and number of impulses presented were sequentially increased throughout the study.
Study sample: Participants were normal-hearing students at the University of Florida who provided written informed consent prior to participation.
Results: TTS was not reliably induced by any of the exposure conditions assessed here. However, there was significant individual variability, and a subset of subjects showed TTS under some exposure conditions.
Conclusions: A subset of participants demonstrated reliable threshold shifts under some conditions. Additional experiments are needed to better understand and optimize stimulus parameters that influence TTS after simulated impulse noise.
Figures


References
-
- Agrawal Y, Niparko JK, Dobie RA. Estimating the Effect of Occupational Noise Exposure on Hearing Thresholds: The Importance of Adjusting for Confounding Variables. Ear Hear. 2010;32:234–237. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal Y, Platz EA, Niparko JK. Risk factors for hearing loss in US adults: data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1999 to 2002. Otol Neurotol. 2009;30:139–145. - PubMed
-
- Ahroon WA, Hill ME, Goodes DP. Analysis of army-wide hearing conservation database for hearing profiles related to crew-served and individual weapon systems. Noise Health. 2011;13:76–83. - PubMed
-
- Attias J, Sapir S, Bresloff I, Reshef-Haran I, Ising H. Reduction in noise-induced temporary threshold shift in humans following oral magnesium intake. Clin Otolaryngol. 2004;29:635–641. - PubMed
-
- Balatsouras DG, Tsimpiris N, Korres S, Karapantzos I, Papadimitriou N, et al. The effect of impulse noise on distortion product otoacoustic emissions. Int J Audiol. 2005;44:540–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
